PCR-targeted Streptomyces gene replacement identifies a protein domain needed for biosynthesis of the sesquiterpene soil odor geosmin
- PMID: 12563033
- PMCID: PMC149868
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0337542100
PCR-targeted Streptomyces gene replacement identifies a protein domain needed for biosynthesis of the sesquiterpene soil odor geosmin
Abstract
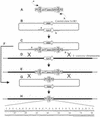
Streptomycetes are high G+C Gram-positive, antibiotic-producing, mycelial soil bacteria. The 8.7-Mb Streptomyces coelicolor genome was previously sequenced by using an ordered library of Supercos-1 clones. Here, we describe an efficient procedure for creating precise gene replacements in the cosmid clones by using PCR targeting and lambda-Red-mediated recombination. The cloned Streptomyces genes are replaced with a cassette containing a selectable antibiotic resistance and oriT(RK2) for efficient transfer to Streptomyces by RP4-mediated intergeneric conjugation. Supercos-1 does not replicate in Streptomyces, but the clones readily undergo double-crossover recombination, thus creating gene replacements. The antibiotic resistance cassettes are flanked by yeast FLP recombinase target sequences for removal of the antibiotic resistance and oriT(RK2) to generate unmarked, nonpolar mutations. The technique has been used successfully by >20 researchers to mutate around 100 Streptomyces genes. As an example, we describe its application to the discovery of a gene involved in the production of geosmin, the ubiquitous odor of soil. The gene, Sco6073 (cyc2), codes for a protein with two sesquiterpene synthase domains, only one of which is required for geosmin biosynthesis, probably via a germacra-1 (10) E,5E-dien-11-ol intermediate generated by the sesquiterpene synthase from farnesyl pyrophosphate.
Figures

References
-
- Bentley S D, Chater K F, Cerdeno-Tarraga A M, Challis G L, Thomson N R, James K D, Harris D E, Quail M A, Kieser H, Harper D, et al. Nature. 2002;417:141–147. - PubMed
-
- Kieser T, Bibb M J, Buttner M J, Chater K F, Hopwood D A. Practical Streptomyces Genetics. Norwich, U.K.: John Innes Foundation; 2000.
-
- Zhang Y, Muyrers J P, Testa G, Stewart A F. Nat Biotechnol. 2000;18:1314–1317. - PubMed
-
- Muyrers J P, Zhang Y, Stewart A F. Genet Eng. 2000;22:77–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

