Role of a single aquaporin isoform in root water uptake
- PMID: 12566588
- PMCID: PMC141217
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.008888
Role of a single aquaporin isoform in root water uptake
Abstract
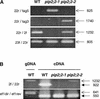
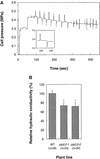
Aquaporins are ubiquitous channel proteins that facilitate the transport of water across cell membranes. Aquaporins show a typically high isoform multiplicity in plants, with 35 homologs in Arabidopsis. The integrated function of plant aquaporins and the function of each individual isoform remain poorly understood. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight analyses suggested that Plasma Membrane Intrinsic Protein2;2 (PIP2;2) is one of the abundantly expressed aquaporin isoforms in Arabidopsis root plasma membranes. Two independent Arabidopsis knockout mutants of PIP2;2 were isolated using a PCR-based strategy from a library of plant lines mutagenized by the insertion of Agrobacterium tumefaciens T-DNA. Expression in transgenic Arabidopsis of a PIP2;2 promoter-beta-glucuronidase gene fusion indicated that PIP2;2 is expressed predominantly in roots, with a strong expression in the cortex, endodermis, and stele. The hydraulic conductivity of root cortex cells, as measured with a cell pressure probe, was reduced by 25 to 30% in the two allelic PIP2;2 mutants compared with the wild type. In addition, free exudation measurements revealed a 14% decrease, with respect to wild-type values, in the osmotic hydraulic conductivity of roots excised from the two PIP2;2 mutants. Together, our data provide evidence for the contribution of a single aquaporin gene to root water uptake and identify PIP2;2 as an aquaporin specialized in osmotic fluid transport. PIP2;2 has a close homolog, PIP2;3, showing 96.8% amino acid identity. The phenotype of PIP2;2 mutants demonstrates that, despite their high homology and isoform multiplicity, plant aquaporins have evolved with nonredundant functions.
Figures




References
-
- Agre, P., Bonhivers, M., and Borgnia, M.J. (1998). The aquaporins, blueprints for cellular plumbing systems. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 14659–14662. - PubMed
-
- Axelos, M., Bardet, C., Liboz, T., Le Van Thai, A., Curie, C., and Lescure, B. (1989). The gene family encoding the Arabidopsis thaliana translation elongation factor EF-1α: Molecular cloning, characterization and expression. Mol. Gen. Genet. 219, 106–112. - PubMed
-
- Barrieu, F., Morillon, R., and Chrispeels, M. (2000). Modulation of aquaporin gene expression in Arabidopsis leads to altered membrane water permeability. In Molecular Biology and Physiology of Water and Solute Transport, S. Hohmann and S. Nielsen, eds (New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers), pp. 255–259.
-
- Bechtold, N., Ellis, J., and Pelletier, G. (1993). In planta Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer by infiltration of adult Arabidopsis thaliana plants. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 316, 1194–1199.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

