Heat and osmotic stress responses of probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 (DR20) in relation to viability after drying
- PMID: 12571012
- PMCID: PMC143580
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.69.2.917-925.2003
Heat and osmotic stress responses of probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 (DR20) in relation to viability after drying
Abstract
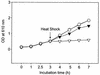
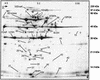
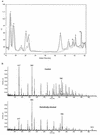
The viability of lactic acid bacteria in frozen, freeze-dried, and air-dried forms is of significant commercial interest to both the dairy and food industries. In this study we observed that when prestressed with either heat (50 degrees C) or salt (0.6 M NaCl), Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 (also known as DR20) showed significant (P < 0.05) improvement in viability compared with the nonstressed control culture after storage at 30 degrees C in the dried form. To investigate the mechanisms underlying this stress-related viability improvement in L. rhamnosus HN001, we analyzed protein synthesis in cultures subjected to different growth stages and stress conditions, using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and N-terminal sequencing. Several proteins were up- or down-regulated after either heat or osmotic shock treatments. Eleven proteins were positively identified, including the classical heat shock proteins GroEL and DnaK and the glycolytic enzymes glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, lactate dehydrogenase, enolase, phosphoglycerate kinase, and triose phosphate isomerase, as well as tagatose 1,6-diphosphate aldolase of the tagatose pathway. The phosphocarrier protein HPr (histidine-containing proteins) was up-regulated in cultures after the log phase irrespective of the stress treatments used. The relative synthesis of an ABC transport-related protein was also up-regulated after shock treatments. Carbohydrate analysis of cytoplasmic contents showed higher levels (20 +/- 3 microg/mg of protein) in cell extracts (CFEs) derived from osmotically stressed cells than in the unstressed control (15 +/- 3 microg/mg of protein). Liquid chromatography of these crude carbohydrate extracts showed significantly different profiles. Electrospray mass spectrometry analysis of CFEs revealed, in addition to normal mono-, di-, tri-, and tetrasaccharides, the presence of saccharides modified with glycerol.
Figures





References
-
- Ang, D., K. Libereck, D. Skowyra, M. Zylicz, and C. Georgopoulos. 1991. Biological role and regulation of the universally conserved heat shock proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 266:24233-24236. - PubMed
-
- Branny, P., F. de la Torre, and J. R. Garel. 1998. An operon encoding three glycolytic enzymes in L. delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, phosphoglycerate kinase and triosephosphate isomerase. Microbiology 144:905-914. - PubMed
-
- Brassart, D., and E. Schiffirin. 1997. The use of probiotics to reinforce mucosal defence mechanisms. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 8:321-326.
-
- Broadbent, J. R., C. J. Oberg, C. Wang, and L. Wei. 1997. Attributes of heat shock response in three species of dairy Lactobacillus. Sys. Appl. Microbiol. 20:12-19.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

