Mechanism of the spatio-temporal regulation of Ras and Rap1
- PMID: 12574122
- PMCID: PMC145447
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg087
Mechanism of the spatio-temporal regulation of Ras and Rap1
Abstract
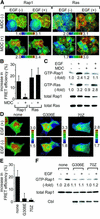
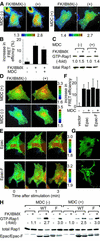
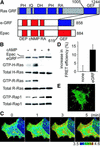
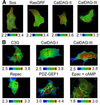
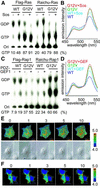
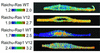
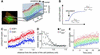
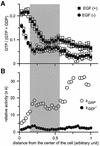
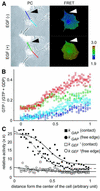
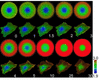
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) activates Ras and Rap1 at distinct intracellular regions. Here, we explored the mechanism underlying this phenomenon. We originally noticed that in cells expressing Epac, a cAMP-dependent Rap1 GEF (guanine nucleotide exchange factor), cAMP activated Rap1 at the perinuclear region, as did EGF. However, in cells expressing e-GRF, a recombinant cAMP-responsive Ras GEF, cAMP activated Ras at the peripheral plasma membrane. Based on the uniform cytoplasmic expression of Epac and e-GRF, GEF did not appear to account for the non-uniform increase in the activities of Ras and Rap1. In contrast, when we used probes with reduced sensitivity to GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs), both Ras and Rap1 appeared to be activated uniformly in the EGF-stimulated cells. Furthermore, we calculated the local rate constants of GEFs and GAPs from the video images of Ras activation and found that GAP activity was higher at the central plasma membrane than the periphery. Thus we propose that GAP primarily dictates the spatial regulation of Ras family G proteins, whereas GEF primarily determines the timing of Ras activation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spatio-temporal images of growth-factor-induced activation of Ras and Rap1.Nature. 2001 Jun 28;411(6841):1065-8. doi: 10.1038/35082594. Nature. 2001. PMID: 11429608
-
Epac is a Rap1 guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor directly activated by cyclic AMP.Nature. 1998 Dec 3;396(6710):474-7. doi: 10.1038/24884. Nature. 1998. PMID: 9853756
-
Identification of guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) for the Rap1 GTPase. Regulation of MR-GEF by M-Ras-GTP interaction.J Biol Chem. 2000 Nov 10;275(45):34901-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M005327200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10934204
-
Ras and Rap1: two highly related small GTPases with distinct function.Exp Cell Res. 1999 Nov 25;253(1):157-65. doi: 10.1006/excr.1999.4695. Exp Cell Res. 1999. PMID: 10579920 Review.
-
The role of Rap1 in integrin-mediated cell adhesion.Biochem Soc Trans. 2003 Feb;31(Pt 1):83-6. doi: 10.1042/bst0310083. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003. PMID: 12546659 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of H-Ras in the endoplasmic reticulum by the RasGRF family guanine nucleotide exchange factors.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Feb;24(4):1516-30. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.4.1516-1530.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 14749369 Free PMC article.
-
The Ras-PI3K signaling pathway is involved in clathrin-independent endocytosis and the internalization of influenza viruses.PLoS One. 2011 Jan 20;6(1):e16324. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016324. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21283725 Free PMC article.
-
Modifying Rap1-signalling by targeting Pde6δ is neuroprotective in models of Alzheimer's disease.Mol Neurodegener. 2018 Sep 26;13(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s13024-018-0283-3. Mol Neurodegener. 2018. PMID: 30257685 Free PMC article.
-
Plexins are GTPase-activating proteins for Rap and are activated by induced dimerization.Sci Signal. 2012 Jan 17;5(207):ra6. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2002636. Sci Signal. 2012. PMID: 22253263 Free PMC article.
-
Ras, an actor on many stages: posttranslational modifications, localization, and site-specified events.Genes Cancer. 2011 Mar;2(3):182-94. doi: 10.1177/1947601911409213. Genes Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21779492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams S.R., Harootunian,A.T., Buechler,Y.J., Taylor,S.S. and Tsien,R.Y. (1991) Fluorescence ratio imaging of cyclic AMP in single cells. Nature, 349, 694–697. - PubMed
-
- Bos J.L. (1997) Ras-like GTPases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1333, M19–M31. - PubMed
-
- Bourne H.R., Sanders,D.A. and McCormick,F. (1990) The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature, 348, 125–132. - PubMed
-
- Brightman F.A. and Fell,D.A. (2000) Differential feedback regulation of the MAPK cascade underlies the quantitative differences in EGF and NGF signalling in PC12 cells. FEBS Lett., 482, 169–174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

