Quantitative assay of hepatitis C virus RNA using an automated extraction system for specific capture with probes and paramagnetic particle separation
- PMID: 12574248
- PMCID: PMC149669
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.2.572-575.2003
Quantitative assay of hepatitis C virus RNA using an automated extraction system for specific capture with probes and paramagnetic particle separation
Abstract
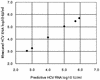
A commercially available automated specimen preparation instrument for specific probe capture and paramagnetic separation has been developed (AmpliCap/GT-12; Roche Molecular Systems). We evaluated assay performance of the AmpliCap/GT-12 in the quantitative assay for hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA with the AMPLICOR HCV MONITOR Test (version 2.0). Assay linearity using serial dilutions from a serum panel was observed in the range of 500 to 850000 IU/ml, with a slightly compromised slope in the higher viral titers. The overall within-run and between-run reproducibility of the entire detection process for 3 and 5 log(10) (IU/ml) of HCV RNA in samples had a standard deviation of <0.2, which was comparable to a manual method based on organic extraction and isopropanol precipitation (Roche Molecular Systems). Comparison of the test results with those obtained by the manual method showed a good correlation (R(2) = 0.972, n = 86). Using heparin (3, 6.5, and 13 U/ml), dextran sulfate (0.1, 1, and 5 mM), hemoglobin (1.13, 2.25, and 4.5 g/liter), conjugated or unconjugated bilirubin (7.5, 15, and 30 mg/dl), and ATP (1.25, 2.5, and 5.0 mM) as known inhibitors, inhibition was only detected at a dextran sulfate concentration of 1 mM with the manual method but not with the AmpliCap/GT-12 extraction. In summary, the AmpliCap/GT-12 system was shown to permit a stable extraction process and accurate results for the quantitative assay of HCV RNA, successfully eliminating the inhibitory effect of dextran sulfate. This automated extraction system provides reliable and reproducible test results and saves labor; thus, it is suitable for routine diagnostic PCR.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Automated specific capture of hepatitis C virus RNA with probes and paramagnetic particle separation.J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Jan;38(1):18-21. doi: 10.1128/JCM.38.1.18-21.2000. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10618056 Free PMC article.
-
[Inhibitory effects of therapeutic reagents on the PCR detection of hepatitis C virus in serum and their elimination by RNA extraction methods].Rinsho Byori. 1999 Oct;47(10):949-55. Rinsho Byori. 1999. PMID: 10590669 Japanese.
-
[Examination of HCV infection in hemodialysis patients with HCV-RNA assay using a magnetic extraction method (AmpliCap GT HCV MONITOR Test Kit v2.0 and AmpliCap GT HCV Specimen Preparation Kit v2.0)].Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 2003;45(2):91-7. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 2003. PMID: 12703404 Japanese.
-
Evaluation of the MagNA pure LC instrument for extraction of hepatitis C virus RNA for the COBAS AMPLICOR Hepatitis C Virus Test, version 2.0.J Clin Microbiol. 2003 Aug;41(8):3503-8. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.8.3503-3508.2003. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12904346 Free PMC article.
-
Automation of laboratory testing for infectious diseases using the polymerase chain reaction-- our past, our present, our future.J Clin Virol. 2001 Jan;20(1-2):1-6. doi: 10.1016/s1386-6532(00)00148-7. J Clin Virol. 2001. PMID: 11163576 Review.
Cited by
-
Extraction of HCV-RNA from Plasma Samples: Development towards Semiautomation.Int J Anal Chem. 2015;2015:367801. doi: 10.1155/2015/367801. Epub 2015 Mar 19. Int J Anal Chem. 2015. PMID: 25873968 Free PMC article.
-
The role of human metapneumovirus in upper respiratory tract infections in children: a 20-year experience.J Infect Dis. 2006 Feb 1;193(3):387-95. doi: 10.1086/499274. Epub 2005 Dec 30. J Infect Dis. 2006. PMID: 16388486 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrams, D. I., S. Kuno, R. Wong, K. Jeffords, M. Nash, J. B. Molaghan, et al. 1989. Oral dextran sulfate (UA001) in the treatment of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and AIDS-related complex. Ann. Intern. Med. 110:183-188. - PubMed
-
- Bruno, R., P. Sacchi, M. Puoti, V. Soriano, and G. Filice. 2002. HCV chronic hepatitis in patients with HIV. Clinical management issues. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 97:1598-1606. - PubMed
-
- Carreno, V. 2002. Present treatment expectations and risks of chronic hepatitis C. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 8:74-79. - PubMed
-
- Castro, F. J., J. I. Seteban, A. Juarez, S. Sauleda, L. Viladomiu, M. Martell, F. Moreno, H. Allende, R. Esteban, and J. Guardia. 2002. Early detection of nonresponse to interferon plus ribavirin combination treatment of chronic hepatitis C. J. Viral Hepat. 9:202-207. - PubMed
-
- Demeke, T., and R. P. Adams. 1992. The effects of plant polysaccharides and buffer additives on PCR. BioTechniques 12:322-324. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

