Apophysomyces elegans: an emerging zygomycete in India
- PMID: 12574283
- PMCID: PMC149688
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.2.783-788.2003
Apophysomyces elegans: an emerging zygomycete in India
Abstract
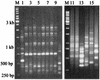
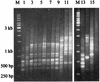
Apophysomyces elegans was considered a rare but medically important zygomycete. We analyzed the clinical records of eight patients from a single center in whom zygomycosis due to A. elegans was diagnosed over a span of 25 months. We also attempted a DNA-based method for rapid identification of the fungi and looked for interstrain polymorphism using microsattelite primers. Three patients had cutaneous and subcutaneous infections, three had isolated renal involvement, one had rhino-orbital tissue infection, and the final patient had a disseminated infection involving the spleen and kidney. Underlying illnesses were found in two patients, one with diabetes mellitus and the other with chronic alcoholism. A history of traumatic implantation was available for three patients. All except two of the patients responded to surgical and/or medical therapy; the diagnosis for the two exceptions was made at the terminal stage of infection. Restriction enzyme (MboI, MspI, HinfI) digestion of the PCR-amplified internal transcribed spacer region helped with the rapid and specific identification of A. elegans. The strains could be divided into two groups according to their patterns, with clustering into one pattern obtained by using microsatellite [(GTG)(5) and (GAC)(5)] PCR fingerprinting. The study highlights the epidemiology, clinical spectrum, and diagnosis of emerging A. elegans infections.
Figures

References
-
- Adam, R. D., G. Hunter, J. DiTomasso, and G. Comerci, Jr. 1994. Mucormycosis; emerging prominence of cutaneous infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 19:67-76. - PubMed
-
- Caceres, A. M., C. Sardina, C. Marcano, R. Guevara, J. Barros, G. Bianchi, V. Rosario, R. Balza, M. Silva, M. C. Redondo, and M. Nunez. 1997. Apophysomyces elegans limb infection with a favorable outcome: case report and review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 25:331-332. - PubMed
-
- Chakrabarti, A., A. Das, A. Sharma, N. Panda, S. Das, K. L. Gupta, and V. Sakhuja. 2001. Ten years' experience in zygomycosis at a tertiary care centre in India. J. Infect. 42:261-266. - PubMed
-
- Chakrabarti, A., P. Kumar, A. A. Padhye, L. Chatha, S. K. Singh, A. Das, J. D. Wig, and R. N. Kataria. 1997. Primary cutaneous zygomycosis due to Saksenaea vasiformis and Apophysomyces elegans. Clin. Infect. Dis. 24:580-583. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

