Early exposure to common anesthetic agents causes widespread neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain and persistent learning deficits
- PMID: 12574416
- PMCID: PMC6741934
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-03-00876.2003
Early exposure to common anesthetic agents causes widespread neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain and persistent learning deficits
Abstract
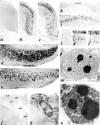
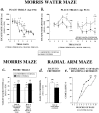
Recently it was demonstrated that exposure of the developing brain during the period of synaptogenesis to drugs that block NMDA glutamate receptors or drugs that potentiate GABA(A) receptors can trigger widespread apoptotic neurodegeneration. All currently used general anesthetic agents have either NMDA receptor-blocking or GABA(A) receptor-enhancing properties. To induce or maintain a surgical plane of anesthesia, it is common practice in pediatric or obstetrical medicine to use agents from these two classes in combination. Therefore, the question arises whether this practice entails significant risk of inducing apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing human brain. To begin to address this problem, we have administered to 7-d-old infant rats a combination of drugs commonly used in pediatric anesthesia (midazolam, nitrous oxide, and isoflurane) in doses sufficient to maintain a surgical plane of anesthesia for 6 hr, and have observed that this causes widespread apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing brain, deficits in hippocampal synaptic function, and persistent memory/learning impairments.
Figures

References
-
- Aggleton JP, Brown MW. Episodic memory, amnesia, and the hippocampal-anterior thalamic axis. Behav Brain Sci. 1999;22:425–489. - PubMed
-
- Corso TD, Sesma MA, Tenkova TI, Der TC, Wozniak DF, Farber NB, Olney JW. Multifocal brain damage induced by phencyclidine is augmented by pilocarpine. Brain Res. 1997;33:533–541. - PubMed
-
- DeOlmos JS, Ingram WR. An improved cupric-silver method for impregnation of axonal and terminal degeneration. Brain Res. 1971;33:523–529. - PubMed
-
- Dikranian K, Ishimaru MJ, Tenkova T, Labruyere J, Qin YQ, Ikonomidou C, Olney JW. Apoptosis in the in vivo mammalian forebrain. Neurobiol Dis. 2001;8:359–379. - PubMed
-
- Dobbing J, Sands J. The brain growth spurt in various mammalian species. Early Hum Dev. 1979;3:79–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AG 11355/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG011355/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 DA000406/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD037100/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- MH 45493/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG018434/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HD 37100/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA012951/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AG 18434/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DA 05072/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DA 00406/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- AA 12951/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH045493/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HD037100/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA005072/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
