Tissue-specific reduction in splicing efficiency of IKBKAP due to the major mutation associated with familial dysautonomia
- PMID: 12577200
- PMCID: PMC1180251
- DOI: 10.1086/368263
Tissue-specific reduction in splicing efficiency of IKBKAP due to the major mutation associated with familial dysautonomia
Abstract
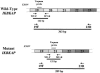
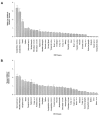
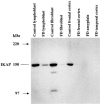
We recently identified a mutation in the I-kappa B kinase associated protein (IKBKAP) gene as the major cause of familial dysautonomia (FD), a recessive sensory and autonomic neuropathy. This alteration, located at base pair 6 of the intron 20 donor splice site, is present on >99.5% of FD chromosomes and results in tissue-specific skipping of exon 20. A second FD mutation, a missense change in exon 19 (R696P), was seen in only four patients heterozygous for the major mutation. Here, we have further characterized the consequences of the major mutation by examining the ratio of wild-type to mutant (WT:MU) IKBKAP transcript in EBV-transformed lymphoblast lines, primary fibroblasts, freshly collected blood samples, and postmortem tissues from patients with FD. We consistently found that WT IKBKAP transcripts were present, albeit to varying extents, in all cell lines, blood, and postmortem FD tissues. Further, a corresponding decrease in the level of WT protein is seen in FD cell lines and tissues. The WT:MU ratio in cultured lymphoblasts varied with growth phase but not with serum concentration or inclusion of antibiotics. Using both densitometry and real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction, we found that relative WT:MU IKBKAP RNA levels were highest in cultured patient lymphoblasts and lowest in postmortem central and peripheral nervous tissues. These observations suggest that the relative inefficiency of WT IKBKAP mRNA production from the mutant alleles in the nervous system underlies the selective degeneration of sensory and autonomic neurons in FD.Therefore, exploration of methods to increase the WT:MU IKBKAP transcript ratio in the nervous system offers a promising approach for developing an effective therapy for patients with FD.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for FD [MIM 223900]) - PubMed
References
-
- Alonso J, Garcia-Miguel P, Abelairas J, Mendiola M, Sarret E, Vendrell MT, Navajas A, Pestana A (2001) Spectrum of germline RB1 gene mutations in Spanish retinoblastoma patients: phenotypic and molecular epidemiological implications. Hum Mutat 17:412–422 - PubMed
-
- Andreassi C, Jarecki J, Zhou J, Coovert DD, Monani UR, Chen X, Whitney M, Pollok B, Zhang M, Androphy E, Burghes AH (2001) Aclarubicin treatment restores SMN levels to cells derived from type I spinal muscular atrophy patients. Hum Mol Genet 10:2841–2849 - PubMed
-
- Axelrod FB (1984) Familial dysautonomia and other congenital and sensory autonomic neuropathies. In: Blake IB (ed) Cell and molecular biology of neuronal development. Plenum Press, New York, pp 331–340
-
- ——— (1995) Familial dysautonomia. In: Robertson D, Biaggioni I (eds) Disorders of the autonomic nervous system. Harwood Academic Publishers, Luxembourg, pp 217–231
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

