Transcriptional profiling of Krüppel-like factor 4 reveals a function in cell cycle regulation and epithelial differentiation
- PMID: 12581631
- PMCID: PMC2693487
- DOI: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)01449-3
Transcriptional profiling of Krüppel-like factor 4 reveals a function in cell cycle regulation and epithelial differentiation
Abstract
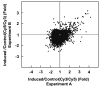
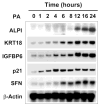
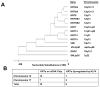
Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) is an epithelially enriched, zinc finger-containing transcription factor, the expression of which is associated with growth arrest. Constitutive expression of KLF4 inhibits G1/S transition of the cell cycle but the manner by which it accomplishes this effect is unclear. To better understand the biochemical function of KLF4, we identified its target genes using cDNA microarray analysis in an established human cell line containing inducible KLF4. RNA extracted from induced and control cells were hybridized differentially to microarray chips containing 9600 human cDNAs. In all, 84 genes with significantly increased expression and 107 genes with significantly reduced expression due to KLF4 induction were identified. The affected genes are sorted to several clusters on the basis of functional relatedness. A major cluster belongs to genes involved in cell-cycle control. Within this cluster, many up-regulated genes are inhibitors of the cell cycle and down-regulated genes are promoters of the cell cycle. Another up-regulated gene cluster includes nine keratin genes, of which seven are located in a specific region on chromosome 12. The results indicate that KLF4 is involved in the control of cell proliferation and does so by eliciting changes in expression of numerous cell-cycle regulatory genes in a concerted manner. Furthermore, KLF4 regulates expression of a group of epithelial-specific keratin genes in a manner consistent with a potential locus control region function.
Figures



References
-
- Marshman E, Booth C, Potten CS. The intestinal epithelial stem cell. BioEssays. 2002;24:91–98. - PubMed
-
- Simon TC, Gordon JI. Intestinal epithelial cell differentiation: new insights from mice, flies and nematodes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995;5:577–586. - PubMed
-
- Gordon JI, Hermiston ML. Differentiation and self-renewal in the mouse gastrointestinal epithelium. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994;6:795–803. - PubMed
-
- Fuchs E, Raghavan S. Getting under the skin of epidermal morphogenesis. Nature Rev Genet. 2002;3:199–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

