Desensitization, internalization, and signaling functions of beta-arrestins demonstrated by RNA interference
- PMID: 12582207
- PMCID: PMC149903
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.262789099
Desensitization, internalization, and signaling functions of beta-arrestins demonstrated by RNA interference
Abstract
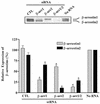
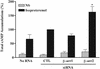
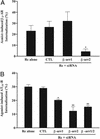
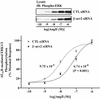
Beta-arrestins bind to activated G protein-coupled receptor kinase-phosphorylated receptors, which leads to their desensitization with respect to G proteins, internalization via clathrin-coated pits, and signaling via a growing list of "scaffolded" pathways. To facilitate the discovery of novel adaptor and signaling roles of beta-arrestins, we have developed and validated a generally applicable interfering RNA approach for selectively suppressing beta-arrestins 1 or 2 expression by up to 95%. Beta-arrestin depletion in HEK293 cells leads to enhanced cAMP generation in response to beta(2)-adrenergic receptor stimulation, markedly reduced beta(2)-adrenergic receptor and angiotensin II receptor internalization and impaired activation of the MAP kinases ERK 1 and 2 by angiotensin II. This approach should allow discovery of novel signaling and regulatory roles for the beta-arrestins in many seven-membrane-spanning receptor systems.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

