Evolution of transcription factors and the gene regulatory network in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 12582243
- PMCID: PMC150228
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg210
Evolution of transcription factors and the gene regulatory network in Escherichia coli
Abstract
The most detailed information presently available for an organism's transcriptional regulation network is that for the prokaryote Escherichia coli. In order to gain insight into the evolution of the E.coli regulatory network, we analysed information obtainable for the domains and protein families of the transcription factors and regulated genes. About three-quarters of the 271 transcription factors we identified are two-domain proteins, consisting of a DNA-binding domain along with a regulatory domain. The regulatory domains mainly bind small molecules. Many groups of transcription factors have identical domain architectures, and this implies that roughly three-quarters of the transcription factors have arisen as a consequence of gene duplication. In contrast, there is little evidence of duplication of regulatory regions together with regulated genes or of transcription factors together with regulated genes. Thirty-eight, out of the 121 transcription factors for which one or more regulated genes are known, regulate other transcription factors. This amplification effect, as well as large differences between the numbers of genes directly regulated by transcription factors, means that there are about 10 global regulators which each control many more genes than the other transcription factors.
Figures
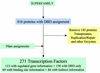





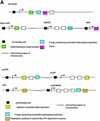


References
-
- Perez-Rueda E. and Collado-Vides,J. (2001) Common history at the origin of the position-function correlation in transcriptional regulators in archaea and bacteria. J. Mol. Evol., 53, 172–179. - PubMed
-
- Thieffry D., Huerta,A.M., Perez-Rueda,E. and Collado-Vides,J. (1998) From specific gene regulation to genomic networks: a global analysis of transcriptional regulation in Escherichia coli. Bioessays, 20, 433–440. - PubMed
-
- Shen-Orr S.S., Milo,R., Mangan,S. and Alon,U. (2002) Network motifs in the transcriptional regulation network of Escherichia coli. Nature Genet., 31, 64–68. - PubMed
-
- Guelzim N., Bottani,S., Bourgine,P. and Kepes,F. (2002) Topological and causal structure of the yeast transcriptional regulatory network. Nature Genet., 31, 60–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

