A promoter activity is present in the DNA sequence corresponding to the hepatitis C virus 5' UTR
- PMID: 12582247
- PMCID: PMC150218
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg199
A promoter activity is present in the DNA sequence corresponding to the hepatitis C virus 5' UTR
Abstract
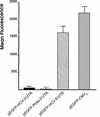
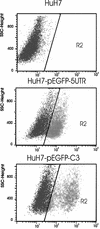
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) 5' untranslated region (UTR) has been extensively studied with regard to its internal ribosomal entry site (IRES) activity. In this work we present results suggesting the existence of a strong promoter activity carried by the DNA sequence corresponding to the HCV 5' UTR. This activity was not detected when the HCV 5' UTR sequence was replaced by HCV 3' UTR or poliovirus 5' UTR sequences. These results were further confirmed by using bicistronic constructions. We demonstrated the presence of an mRNA initiated in this 5' UTR sequence and located the initiation site by the 5' RACE method at nucleotide 67. Furthermore, northern experiments and flow cytometry analysis showed the unambiguous activity of such a promoter sequence in stably transfected cells. Our results strongly suggest that the data obtained using bicistronic DNA constructs carrying the HCV 5' UTR should be analyzed not only at the translational but also at the transcriptional level.
Figures




References
-
- WHO (2000) Hepatitis C Fact Sheet No. 164, revised October 2000.
-
- Honda M., Ping,L.H., Rijnbrand,R.C., Amphlett,E., Clarke,B., Rowlands,D. and Lemon,S.M. (1996) Structural requirements for initiation of translation by internal ribosome entry within genome-length hepatitis C virus RNA. Virology, 222, 31–42. - PubMed
-
- Odreman-Macchioli F., Baralle,F.E. and Buratti,E. (2001) Mutational analysis of the different bulge regions of the HCV domain II and their influence on IRES translational ability. J. Biol. Chem., 276, 41648–41655. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka T., Kato,N., Cho,M.J. and Shimotohno,K. (1995) A novel sequence found at the 3′ terminus of hepatitis C virus genome. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 215, 744–749. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

