Simian virus 40 small tumor antigen induces deregulation of the actin cytoskeleton and tight junctions in kidney epithelial cells
- PMID: 12584304
- PMCID: PMC149746
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.5.2807-2818.2003
Simian virus 40 small tumor antigen induces deregulation of the actin cytoskeleton and tight junctions in kidney epithelial cells
Abstract
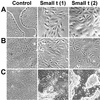
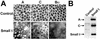
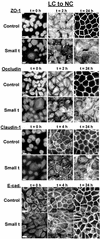
There is increasing evidence that the transforming DNA tumor virus simian virus 40 (SV40) is associated with human malignancies. SV40 small tumor antigen (small t) interacts with endogenous serine/threonine protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) and is required for the transforming activity of SV40 in epithelial cells of the lung and kidney. Here, we show that expression of SV40 small t in epithelial MDCK cells induces acute morphological changes and multilayering. Significantly, it also causes severe defects in the biogenesis and barrier properties of tight junctions (TJs) but does not prevent formation of adherens junctions. Small t-induced TJ defects are associated with a loss of PP2A from areas of cell-cell contact; altered distribution and reduced amounts of the TJ proteins ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-1; and marked disorganization of the actin cytoskeleton. Small t-mediated F-actin rearrangements encompass increased Rac-induced membrane ruffling and lamellipodia, Cdc42-initiated filopodia, and loss of Rho-dependent stress fibers. Indeed, these F-actin changes coincide with elevated levels of Rac1 and Cdc42 and decreased amounts of RhoA in small t-expressing cells. Notably, these cellular effects of small t are dependent on its interaction with endogenous PP2A. Thus, our findings provide the first evidence that, in polarized epithelial cells, expression of small t alone is sufficient to induce deregulation of Rho GTPases, F-actin, and intercellular adhesion, through interaction with endogenous PP2A. Because defects in the actin cytoskeleton and TJ disruption have been linked to loss of cell polarity and tumor invasiveness, their deregulation by PP2A and small t likely contributes to the role of SV40 in epithelial cell transformation.
Figures






Similar articles
-
RhoA, Rac1, and Cdc42 exert distinct effects on epithelial barrier via selective structural and biochemical modulation of junctional proteins and F-actin.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004 Aug;287(2):C327-35. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00087.2004. Epub 2004 Mar 24. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15044152
-
Constitutive activation of Rho proteins by CNF-1 influences tight junction structure and epithelial barrier function.J Cell Sci. 2003 Feb 15;116(Pt 4):725-42. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00300. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 12538773
-
Protein phosphatase 2A associates with and regulates atypical PKC and the epithelial tight junction complex.J Cell Biol. 2002 Sep 2;158(5):967-78. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200206114. Epub 2002 Aug 26. J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12196510 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of cell adhesion by PP2A and SV40 small tumor antigen: an important link to cell transformation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006 Dec;63(24):2979-91. doi: 10.1007/s00018-006-6300-7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006. PMID: 17072501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epithelial junctions and Rho family GTPases: the zonular signalosome.Small GTPases. 2014;5(4):1-15. doi: 10.4161/21541248.2014.973760. Small GTPases. 2014. PMID: 25483301 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic viral infection and primary central nervous system malignancy.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2010 Sep;5(3):387-403. doi: 10.1007/s11481-010-9204-0. Epub 2010 Apr 13. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20387126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rho'ing in and out of cells: viral interactions with Rho GTPase signaling.Small GTPases. 2014;5:e28318. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.28318. Epub 2014 Mar 24. Small GTPases. 2014. PMID: 24691164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small tumor antigen of polyomaviruses: role in viral life cycle and cell transformation.J Cell Physiol. 2008 May;215(2):309-19. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21326. J Cell Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18022798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
E7 oncoprotein from human papillomavirus 16 alters claudins expression and the sealing of epithelial tight junctions.Int J Oncol. 2020 Oct;57(4):905-924. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2020.5105. Epub 2020 Jul 29. Int J Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32945372 Free PMC article.
-
Human Papillomavirus E6 interaction with cellular PDZ domain proteins modulates YAP nuclear localization.Virology. 2018 Mar;516:127-138. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2018.01.003. Epub 2018 Jan 12. Virology. 2018. PMID: 29346075 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cereijido, M., L. Shoshani, and R. G. Contreras. 2000. Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of tight junctions. I. Biogenesis of tight junctions and epithelial polarity. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 279:G477-G482. - PubMed
-
- Denker, B. M., and S. K. Nigam. 1998. Molecular structure and assembly of the tight junction. Am. J. Physiol. 274:F1-F9. - PubMed
-
- Evers, E. E., G. C. Zondag, A. Malliri, L. S. Price, J. P. ten Klooster, R. A. van der Kammen, and J. G. Collard. 2000. Rho family proteins in cell adhesion and cell migration. Eur. J. Cancer 36:1269-1274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

