Genetic characterization of rebounding human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in plasma during multiple interruptions of highly active antiretroviral therapy
- PMID: 12584346
- PMCID: PMC149739
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.5.3229-3237.2003
Genetic characterization of rebounding human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in plasma during multiple interruptions of highly active antiretroviral therapy
Abstract
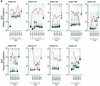
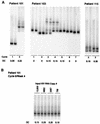
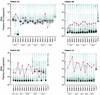
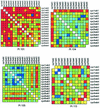
Various strategies of interrupting highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) are being investigated for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Interruptions of greater than 2 weeks frequently result in rebound of plasma HIV RNA. In order to discern changes in the viral population that might occur during cycles of treatment interruption, we evaluated the homology of HIV-1 envelope gene sequences over time in 12 patients who received four to seven cycles of 4 weeks off HAART followed by 8 weeks on HAART by using the heteroduplex tracking assay and novel statistical tools. HIV populations in 9 of 12 patients diverged from those found in the first cycle in at least one subsequent cycle. The substantial genetic changes noted in HIV env did not correlate with increased or decreased log changes in levels of plasma HIV RNA (P > 0.5). Thus, genetic changes in HIV env itself did not contribute in a systematic way to changes in levels of plasma viremia from cycle to cycle of treatment interruption. In addition, the data suggest that there may be multiple compartments contributing to the rebound of plasma viremia and to viral diversity from cycle to cycle of intermittent therapy.
Figures

References
-
- Altfeld, M., and B. D. Walker. 2001. Less is more? STI in acute and chronic HIV-1 infection. Nat. Med. 7:881-884. - PubMed
-
- Behrens, G., A. Dejam, H. Schmidt, H. J. Balks, G. Brabant, T. Korner, M. Stoll, and R. E. Schmidt. 1999. Impaired glucose tolerance, beta cell function and lipid metabolism in HIV patients under treatment with protease inhibitors. AIDS 13:F63-F70. - PubMed
-
- Binswanger, H. P. 2001. Public health. HIV/AIDS treatment for millions. Science 292:221-223. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2000. HIV/AIDS Surveillance Report 12. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Ga.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

