The maize low-phytic acid mutant lpa2 is caused by mutation in an inositol phosphate kinase gene
- PMID: 12586875
- PMCID: PMC166827
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.014258
The maize low-phytic acid mutant lpa2 is caused by mutation in an inositol phosphate kinase gene
Abstract
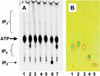
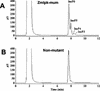
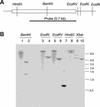
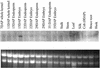
Reduced phytic acid content in seeds is a desired goal for genetic improvement in several crops. Low-phytic acid mutants have been used in genetic breeding, but it is not known what genes are responsible for the low-phytic acid phenotype. Using a reverse genetics approach, we found that the maize (Zea mays) low-phytic acid lpa2 mutant is caused by mutation in an inositol phosphate kinase gene. The maize inositol phosphate kinase (ZmIpk) gene was identified through sequence comparison with human and Arabidopsis Ins(1,3,4)P(3) 5/6-kinase genes. The purified recombinant ZmIpk protein has kinase activity on several inositol polyphosphates, including Ins(1,3,4)P(3), Ins(3,5,6)P(3), Ins(3,4,5,6)P(4), and Ins(1,2,5,6)P(4). The ZmIpk mRNA is expressed in the embryo, the organ where phytic acid accumulates in maize seeds. The ZmIpk Mutator insertion mutants were identified from a Mutator F(2) family. In the ZmIpk Mu insertion mutants, seed phytic acid content is reduced approximately 30%, and inorganic phosphate is increased about 3-fold. The mutants also accumulate myo-inositol and inositol phosphates as in the lpa2 mutant. Allelic tests showed that the ZmIpk Mu insertion mutants are allelic to the lpa2. Southern-blot analysis, cloning, and sequencing of the ZmIpk gene from lpa2 revealed that the lpa2-1 allele is caused by the genomic sequence rearrangement in the ZmIpk locus and the lpa2-2 allele has a nucleotide mutation that generated a stop codon in the N-terminal region of the ZmIpk open reading frame. These results provide evidence that ZmIpk is one of the kinases responsible for phytic acid biosynthesis in developing maize seeds.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The maize low-phytic acid 3 encodes a myo-inositol kinase that plays a role in phytic acid biosynthesis in developing seeds.Plant J. 2005 Jun;42(5):708-19. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02412.x. Plant J. 2005. PMID: 15918884
-
Seed phosphorus and inositol phosphate phenotype of barley low phytic acid genotypes.Phytochemistry. 2003 Mar;62(5):691-706. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9422(02)00610-6. Phytochemistry. 2003. PMID: 12620321
-
Expression and nucleotide sequence of an INS (3) P1 synthase gene associated with low-phytate kernels in maize (Zea mays L.).J Agric Food Chem. 2004 Jul 14;52(14):4565-70. doi: 10.1021/jf049976b. J Agric Food Chem. 2004. PMID: 15237968
-
Mutations in genes controlling the biosynthesis and accumulation of inositol phosphates in seeds.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Apr;38(2):689-94. doi: 10.1042/BST0380689. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 20298244 Review.
-
myo-Inositol-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexakisphosphate.Phytochemistry. 2003 Nov;64(6):1033-43. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9422(03)00446-1. Phytochemistry. 2003. PMID: 14568069 Review.
Cited by
-
The Arabidopsis ATP-binding cassette protein AtMRP5/AtABCC5 is a high affinity inositol hexakisphosphate transporter involved in guard cell signaling and phytate storage.J Biol Chem. 2009 Nov 27;284(48):33614-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.030247. Epub 2009 Sep 21. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19797057 Free PMC article.
-
Can Inositol Pyrophosphates Inform Strategies for Developing Low Phytate Crops?Plants (Basel). 2020 Jan 17;9(1):115. doi: 10.3390/plants9010115. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31963418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Overview of Targeted Genome Editing Strategies for Reducing the Biosynthesis of Phytic Acid: an Anti-nutrient in Crop Plants.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Jan;66(1):11-25. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00722-1. Epub 2023 Apr 16. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37061991 Review.
-
Roles of inositol phosphates and inositol pyrophosphates in development, cell signaling and nuclear processes.Adv Enzyme Regul. 2010;50(1):324-37. doi: 10.1016/j.advenzreg.2009.12.002. Epub 2009 Dec 16. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2010. PMID: 20006638 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Conformational changes in inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate 2-kinase upon substrate binding: role of N-terminal lobe and enantiomeric substrate preference.J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 24;287(35):29237-49. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.363671. Epub 2012 Jun 28. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22745128 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Biswas BB, Ghosh B, Majumder AL. myo-Inositol polyphosphates and their role in cellular metabolism: a proposed cycle involving glucose-6-phosphate and myo-inositol phosphates. Subcell Biochem. 1984;10:237–280. - PubMed
-
- Bollmann O, Strother S, Hoffmann-Ostenhof O. The enzymes involved in the synthesis of phytic acid in Lemna gibba: studies on the biosynthesis of cyclitols, XL. Mol Cell Biochem. 1980;30:171–175. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

