The formation of skeletal muscle: from somite to limb
- PMID: 12587921
- PMCID: PMC1571050
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1469-7580.2003.00139.x
The formation of skeletal muscle: from somite to limb
Abstract
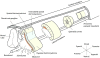
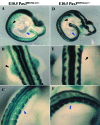
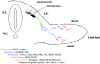
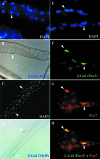
During embryogenesis, skeletal muscle forms in the vertebrate limb from progenitor cells originating in the somites. These cells delaminate from the hypaxial edge of the dorsal part of the somite, the dermomyotome, and migrate into the limb bud, where they proliferate, express myogenic determination factors and subsequently differentiate into skeletal muscle. A number of regulatory factors involved in these different steps have been identified. These include Pax3 with its target c-met, Lbx1 and Mox2 as well as the myogenic determination factors Myf5 and MyoD and factors required for differentiation such as Myogenin, Mrf4 and Mef2 isoforms. Mutants for genes such as Lbx1 and Mox2, expressed uniformly in limb muscle progenitors, reveal unexpected differences between fore and hind limb muscles, also indicated by the differential expression of Tbx genes. As development proceeds, a secondary wave of myogenesis takes place, and, postnatally, satellite cells become located under the basal lamina of adult muscle fibres. Satellite cells are thought to be the progenitor cells for adult muscle regeneration, during which similar genes to those which regulate myogenesis in the embryo also play a role. In particular, Pax3 as well as its orthologue Pax7 are important. The origin of secondary/fetal myoblasts and of adult satellite cells is unclear, as is the relation of the latter to so-called SP or stem cell populations, or indeed to potential mesangioblast progenitors, present in blood vessels. The oligoclonal origin of postnatal muscles points to a small number of founder cells, whether or not these have additional origins to the progenitor cells of the somite which form the first skeletal muscles, as discussed here for the embryonic limb.
Figures
References
-
- Beauchamp JR, Heslop L, Yu DSW, Kelly RG, Tajbakhsh T, Buckingham ME, et al. Expression of CD34 and Myf5 defines the majority of quiescent adult skeletal muscle satellite cells. J. Cell Biol. 2000;151:1221–1233. 10.1046/j.1469-7580.2003.00139.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Black BL, Olson EN. Transcriptional control of muscle development by myocyte enhancer factor 2 (MEF2) proteins. Ann. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1998;14:167–196. 10.1046/j.1469-7580.2003.00139.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bladt F, Riethmacher D, Isenmann S, Aguzzi A, Birchmeier C. Essential role for the c-met receptor in the migration of myogenic precursor cells into the limb bud. Nature. 1995;376:768–771. 10.1046/j.1469-7580.2003.00139.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Buckingham M. Skeletal muscle formation in vertebrates. Current Opinion Genet. Dev. 2001;11:440–448. 10.1046/j.1469-7580.2003.00139.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Christ B, Ordahl CP. Early stages of chick somite development. Anat. Embryol. 1995;191:381–396. 10.1046/j.1469-7580.2003.00139.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

