Polarization of the C. elegans zygote proceeds via distinct establishment and maintenance phases
- PMID: 12588843
- PMCID: PMC1761648
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.00284
Polarization of the C. elegans zygote proceeds via distinct establishment and maintenance phases
Abstract
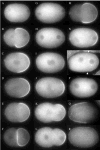
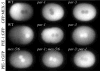
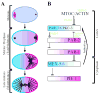
Polarization of the C. elegans zygote along the anterior-posterior axis depends on cortically enriched (PAR) and cytoplasmic (MEX-5/6) proteins, which function together to localize determinants (e.g. PIE-1) in response to a polarizing cue associated with the sperm asters. Using time-lapse microscopy and GFP fusions, we have analyzed the localization dynamics of PAR-2, PAR-6, MEX-5, MEX-6 and PIE-1 in wild-type and mutant embryos. These studies reveal that polarization involves two genetically and temporally distinct phases. During the first phase (establishment), the sperm asters at one end of the embryo exclude the PAR-3/PAR-6/PKC3 complex from the nearby cortex, allowing the ring finger protein PAR-2 to accumulate in an expanding 'posterior' domain. Onset of the establishment phase involves the non-muscle myosin NMY-2 and the 14-3-3 protein PAR-5. The kinase PAR-1 and the CCCH finger proteins MEX-5 and MEX-6 also function during the establishment phase in a feedback loop to regulate growth of the posterior domain. The second phase begins after pronuclear meeting, when the sperm asters begin to invade the anterior. During this phase (maintenance), PAR-2 maintains anterior-posterior polarity by excluding the PAR-3/PAR-6/PKC3 complex from the posterior. These findings provide a model for how PAR and MEX proteins convert a transient asymmetry into a stably polarized axis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Caenorhabditis elegans par-5 gene encodes a 14-3-3 protein required for cellular asymmetry in the early embryo.Dev Biol. 2002 Jan 1;241(1):47-58. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2001.0489. Dev Biol. 2002. PMID: 11784094
-
Coupling between cytoplasmic concentration gradients through local control of protein mobility in the Caenorhabditis elegans zygote.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Sep 1;26(17):2963-70. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-05-0302. Epub 2015 Jul 8. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 26157168 Free PMC article.
-
Symmetry breaking and polarization of the C. elegans zygote by the polarity protein PAR-2.Development. 2010 May;137(10):1669-77. doi: 10.1242/dev.045823. Epub 2010 Apr 14. Development. 2010. PMID: 20392744 Free PMC article.
-
Cell polarity and the cytoskeleton in the Caenorhabditis elegans zygote.Annu Rev Genet. 2003;37:221-49. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.37.110801.142443. Annu Rev Genet. 2003. PMID: 14616061 Review.
-
The PAR network: redundancy and robustness in a symmetry-breaking system.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013 Sep 23;368(1629):20130010. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0010. Print 2013. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24062581 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Early development of the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita.BMC Dev Biol. 2016 Apr 28;16:10. doi: 10.1186/s12861-016-0109-x. BMC Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27122249 Free PMC article.
-
CDC-42 Interactions with Par Proteins Are Critical for Proper Patterning in Polarization.Cells. 2020 Sep 5;9(9):2036. doi: 10.3390/cells9092036. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32899550 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced dosage of pos-1 suppresses Mex mutants and reveals complex interactions among CCCH zinc-finger proteins during Caenorhabditis elegans embryogenesis.Genetics. 2006 Dec;174(4):1933-45. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.052621. Epub 2006 Oct 8. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 17028349 Free PMC article.
-
Cell polarity-dependent centrosome separation in the C. elegans embryo.J Cell Biol. 2019 Dec 2;218(12):4112-4126. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201902109. Epub 2019 Oct 23. J Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31645459 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid diffusion-state switching underlies stable cytoplasmic gradients in the Caenorhabditis elegans zygote.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Sep 4;115(36):E8440-E8449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1722162115. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30042214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boyd L, Guo S, Levitan D, Stinchcomb DT, Kemphues KJ. PAR-2 is asymmetrically distributed and promotes association of P granules and PAR-1 with the cortex in C. elegans embryos. Development. 1996;122:3075–3084. - PubMed
-
- Doe CQ. Cell polarity: the PARty expands. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3:E7–E9. - PubMed
-
- Etemad-Moghadam B, Guo S, Kemphues KJ. Asymmetrically distributed PAR-3 protein contributes to cell polarity and spindle alignment in early C. elegans embryos. Cell. 1995;83:743–752. - PubMed
-
- Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

