MAPK signaling up-regulates the activity of hypoxia-inducible factors by its effects on p300
- PMID: 12588875
- PMCID: PMC4518846
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M209702200
MAPK signaling up-regulates the activity of hypoxia-inducible factors by its effects on p300
Abstract
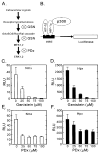
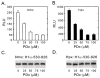
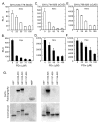
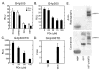
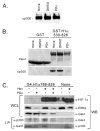
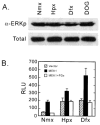
Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF) are a family of heterodimeric transcriptional regulators that play pivotal roles in the regulation of cellular utilization of oxygen and glucose and are essential transcriptional regulators of angiogenesis in solid tumor and ischemic disorders. The transactivation activity of HIF complexes requires the recruitment of p300/CREB-binding protein (CBP) by HIF-1 alpha and HIF-2 alpha that undergo oxygen-dependent degradation. HIF activation in tumors is caused by several factors including mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling. Here we investigated the molecular basis for HIF activation by MAPK. We show that MAPK is required for the transactivation activity of HIF-1 alpha. Furthermore, inhibition of MAPK disrupts the HIF-p300 interaction and suppresses the transactivation activity of p300. Overexpression of MEK1, an upstream MAPK activator, stimulates the transactivation of both p300 and HIF-1 alpha. Interestingly, the C-terminal transactivation domain of HIF-1 alpha is not a direct substrate of MAPK, and HIF-1 alpha phosphorylation is not required for HIF-CAD/p300 interaction. Taken together, our data suggest that MAPK signaling facilitates HIF activation through p300/CBP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hepatitis B virus X protein enhances transcriptional activity of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha through activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway.J Biol Chem. 2003 Oct 3;278(40):39076-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305101200. Epub 2003 Jul 10. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12855680
-
Ca2+/calmodulin kinase-dependent activation of hypoxia inducible factor 1 transcriptional activity in cells subjected to intermittent hypoxia.J Biol Chem. 2005 Feb 11;280(6):4321-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407706200. Epub 2004 Nov 29. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15569687
-
Carboxyl-terminal transactivation activity of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha is governed by a von Hippel-Lindau protein-independent, hydroxylation-regulated association with p300/CBP.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 May;22(9):2984-92. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.9.2984-2992.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11940656 Free PMC article.
-
Erythropoietin gene regulation depends on heme-dependent oxygen sensing and assembly of interacting transcription factors.Kidney Int. 1997 Feb;51(2):548-52. doi: 10.1038/ki.1997.76. Kidney Int. 1997. PMID: 9027736 Review.
-
Roles and signaling pathways of CITED1 in tumors: overview and novel insights.J Int Med Res. 2024 Jan;52(1):3000605231220890. doi: 10.1177/03000605231220890. J Int Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38190845 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Induction of CD36 and thrombospondin-1 in macrophages by hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and its relevance in the inflammatory process.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e48535. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048535. Epub 2012 Oct 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23119050 Free PMC article.
-
Direct phosphorylation events involved in HIF-α regulation: the role of GSK-3β.Hypoxia (Auckl). 2014 Apr 30;2:35-45. doi: 10.2147/HP.S60703. eCollection 2014. Hypoxia (Auckl). 2014. PMID: 27774465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between Hypoxia and Extracellular Matrix in the Tumor Microenvironment in Breast Cancer.Genes (Basel). 2022 Sep 3;13(9):1585. doi: 10.3390/genes13091585. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36140753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of hypoxic signalling in metastasis: towards translating knowledge of basic biology into novel anti-tumour strategies.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2018 Oct;35(7):563-599. doi: 10.1007/s10585-018-9930-x. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2018. PMID: 30171389 Review.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors repress the transactivation potential of hypoxia-inducible factors independently of direct acetylation of HIF-alpha.J Biol Chem. 2006 May 12;281(19):13612-13619. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600456200. Epub 2006 Mar 15. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16543236 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Semenza GL. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1999;15:551–578. - PubMed
-
- Caro J. High Alt Med Biol. 2001;2:145–154. - PubMed
-
- Fedele AO, Whitelaw ML, Peet DJ. Mol Interv. 2002;2:229–243. - PubMed
-
- Huang LE, Arany Z, Livingston DM, Bunn HF. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:32253–32259. - PubMed
-
- Salceda S, Caro J. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:22642–22647. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

