Inhibition of adipogenesis and development of glucose intolerance by soluble preadipocyte factor-1 (Pref-1)
- PMID: 12588883
- PMCID: PMC151920
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI15924
Inhibition of adipogenesis and development of glucose intolerance by soluble preadipocyte factor-1 (Pref-1)
Abstract
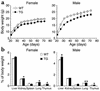
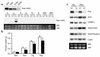
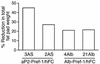
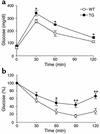
Preadipocyte factor-1 (Pref-1) is a transmembrane protein highly expressed in preadipocytes. Pref-1 expression is, however, completely abolished in adipocytes. The extracellular domain of Pref-1 undergoes two proteolytic cleavage events that generate 50 and 25 kDa soluble products. To understand the function of Pref-1, we generated transgenic mice that express the full ectodomain corresponding to the large cleavage product of Pref-1 fused to human immunoglobulin-gamma constant region. Mice expressing the Pref-1/hFc transgene in adipose tissue, driven by the adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein (aP2, also known as aFABP) promoter, showed a substantial decrease in total fat pad weight. Moreover, adipose tissue from transgenic mice showed reduced expression of adipocyte markers and adipocyte-secreted factors, including leptin and adiponectin, whereas the preadipocyte marker Pref-1 was increased. Pref-1 transgenic mice with a substantial, but not complete, loss of adipose tissue exhibited hypertriglyceridemia, impaired glucose tolerance, and decreased insulin sensitivity. Mice expressing the Pref-1/hFc transgene exclusively in liver under the control of the albumin promoter also showed a decrease in adipose mass and adipocyte marker expression, suggesting an endocrine mode of action of Pref-1. These findings demonstrate the inhibition of adipogenesis by Pref-1 in vivo and the resulting impairment of adipocyte function that leads to the development of metabolic abnormalities.
Figures




References
-
- Faust IM, Johnson PR, Stern JS, Hirsch J. Diet-induced adipocyte number increase in adult rats: a new model of obesity. Am. J. Physiol. 1978;235:E279–E286. - PubMed
-
- Klyde BJ, Hirsch J. Increased cellular proliferation in adipose tissue of adult rats fed a high-fat diet. J. Lipid. Res. 1979;20:705–715. - PubMed
-
- Klyde BJ, Hirsch J. Isotopic labeling of DNA in rat adipose tissue: evidence for proliferating cells associated with mature adipocytes. J. Lipid. Res. 1979;20:691–704. - PubMed
-
- Darlington GJ, Ross SE, MacDougald OA. The role of C/EBP genes in adipocyte differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:30057–30060. - PubMed
-
- MacDougald OA, Mandrup S. Adipogenesis: forces that tip the scales. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2002;13:5–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

