Identification of a structural determinant necessary for the localization and function of estrogen receptor alpha at the plasma membrane
- PMID: 12588983
- PMCID: PMC151696
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.5.1633-1646.2003
Identification of a structural determinant necessary for the localization and function of estrogen receptor alpha at the plasma membrane
Abstract
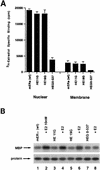
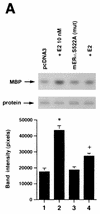
Estrogen receptors (ER) have been localized to the cell plasma membrane (PM), where signal transduction mediates some estradiol (E2) actions. However, the precise structural features of ER that result in membrane localization have not been determined. We obtained a partial tryptic peptide/mass spectrometry analysis of membrane mouse ERalpha protein. Based on this, we substituted alanine for the determined serine at amino acid 522 within the E domain of wild-type (wt) ERalpha. Upon transfection in CHO cells, the S522A mutant ERalpha resulted in a 62% decrease in membrane receptor number and reduced colocalization with caveolin 1 relative to those with expression of wt ERalpha. E2 was significantly less effective in stimulating multiple rapid signals from the membranes of CHO cells expressing ERalpha S522A than from those of CHO cells expressing wt ERalpha. In contrast, nuclear receptor expression and transcriptional function were very similar. The S522A mutant was also 60% less effective than wt ERalpha in binding caveolin 1, which facilitates ER transport to the PM. All functions of ERalpha mutants with other S-to-A substitutions were comparable to those of wt ER, and deletion of the A/B or C domain had little consequence for membrane localization or function. Transfection of ERalpha S522A into breast cancer cells that express native ER downregulated E2 binding at the membrane, signaling to ERK, and G1/S cell cycle events and progression. However, there was no effect on the E2 transactivation of an ERE-luciferase reporter. In summary, serine 522 is necessary for the efficient translocation and function of ERalpha at the PM. The S522A mutant also serves as a dominant-negative construct, identifying important functions of E2 that originate from activating PM ER.
Figures














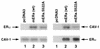



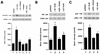




Similar articles
-
Distinctive actions of membrane-targeted versus nuclear localized estrogen receptors in breast cancer cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2005 Jun;19(6):1606-17. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0468. Epub 2005 Apr 14. Mol Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 15831524
-
S-palmitoylation modulates human estrogen receptor-alpha functions.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Apr 9;316(3):878-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.02.129. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. PMID: 15033483
-
Requirements for estrogen receptor alpha membrane localization and function.Steroids. 2005 May-Jun;70(5-7):361-3. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2005.02.015. Epub 2005 Mar 25. Steroids. 2005. PMID: 15862818 Review.
-
ERs associate with and regulate the production of caveolin: implications for signaling and cellular actions.Mol Endocrinol. 2002 Jan;16(1):100-15. doi: 10.1210/mend.16.1.0757. Mol Endocrinol. 2002. PMID: 11773442
-
Membrane association of estrogen receptor alpha and beta influences 17beta-estradiol-mediated cancer cell proliferation.Steroids. 2008 Oct;73(9-10):853-8. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2007.12.003. Epub 2007 Dec 14. Steroids. 2008. PMID: 18206197 Review.
Cited by
-
Distribution and posttranslational modification of synaptic ERα in the adult female rat hippocampus.Endocrinology. 2013 Feb;154(2):819-30. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1870. Epub 2012 Nov 26. Endocrinology. 2013. PMID: 23183182 Free PMC article.
-
Endocrinology and hormone therapy in breast cancer: new insight into estrogen receptor-alpha function and its implication for endocrine therapy resistance in breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2005;7(5):205-11. doi: 10.1186/bcr1287. Epub 2005 Jul 20. Breast Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16168139 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen actions on neuroendocrine glia.Neuroendocrinology. 2010;91(3):211-22. doi: 10.1159/000289568. Epub 2010 Mar 24. Neuroendocrinology. 2010. PMID: 20332598 Free PMC article.
-
Rodent Models of Non-classical Progesterone Action Regulating Ovulation.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2017 Jul 24;8:165. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2017.00165. eCollection 2017. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2017. PMID: 28790975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen Receptor-Dependent Regulation of Dendritic Cell Development and Function.Front Immunol. 2017 Feb 10;8:108. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00108. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28239379 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albanese, C., J. Johnson, G. Watanabe, N. Eklund, D. Vu, A. Arnold, and R. G. Pestell. 1995. Transforming p21 ras mutants and c-Ets-2 activate the cyclin D1 promoter through distinguishable regions. J. Biol. Chem. 270:23589-23597. - PubMed
-
- Alton, G., M. Hasilik, R. Niehues, K. Paneerselvam, J. R. Etchison, F. Fana, and H. H. Freeze. 1998. Direct utilization of mannose for mammalian glycoprotein biosynthesis. Glycobiology 8:285-295. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, R. G. 1998. The caveolae membrane system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67:199-225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
