Synthetic lethal interaction of the mitochondrial phosphatidylethanolamine biosynthetic machinery with the prohibitin complex of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 12589040
- PMCID: PMC149978
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-05-0263
Synthetic lethal interaction of the mitochondrial phosphatidylethanolamine biosynthetic machinery with the prohibitin complex of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
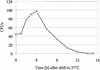
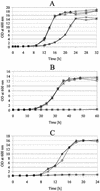
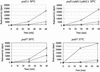
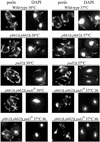
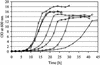
The majority of mitochondrial phosphatidylethanolamine (PtdEtn), a phospholipid essential for aerobic growth of yeast cells, is synthesized by phosphatidylserine decarboxylase 1 (Psd1p) in the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM). To identify components that become essential when the level of mitochondrial PtdEtn is decreased, we screened for mutants that are synthetically lethal with a temperature-sensitive (ts) allele of PSD1. This screen unveiled mutations in PHB1 and PHB2 encoding the two subunits of the prohibitin complex, which is located to the IMM and required for the stability of mitochondrially encoded proteins. Deletion of PHB1 and PHB2 resulted in an increase of mitochondrial PtdEtn at 30 degrees C. On glucose media, phb1Delta psd1Delta and phb2Delta psd1Delta double mutants were rescued only for a limited number of generations by exogenous ethanolamine, indicating that a decrease of the PtdEtn level is detrimental for prohibitin mutants. Similar to phb mutants, deletion of PSD1 destabilizes polypeptides encoded by the mitochondrial genome. In a phb1Delta phb2Delta psd1(ts) strain the destabilizing effect is dramatically enhanced. In addition, the mitochondrial genome is lost in this triple mutant, and nuclear-encoded proteins of the IMM are assembled at a very low rate. At the nonpermissive temperature mitochondria of phb1Delta phb2Delta psd1(ts) were fragmented and aggregated. In conclusion, destabilizing effects triggered by low levels of mitochondrial PtdEtn seem to account for synthetic lethality of psd1Delta with phb mutants.
Figures


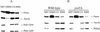
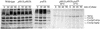

References
-
- Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. New York: John Wiley & Sons; 1996.
-
- Broekhuyse RM. Phospholipids in tissues of the eye. I. Isolation, characterization and quantitative analysis by two-dimensional thin-layer chromatography of diacyl and vinyl-ether phospholipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968;152:307–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

