IKKalpha regulates mitogenic signaling through transcriptional induction of cyclin D1 via Tcf
- PMID: 12589056
- PMCID: PMC149994
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.02-06-0101
IKKalpha regulates mitogenic signaling through transcriptional induction of cyclin D1 via Tcf
Abstract
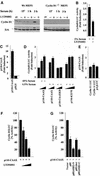
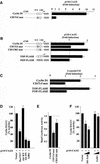
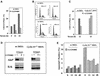
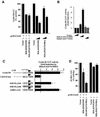
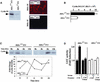
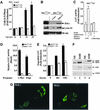
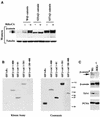
The Wnt/beta-catenin/Tcf and IkappaB/NF-kappaB cascades are independent pathways involved in cell cycle control, cellular differentiation, and inflammation. Constitutive Wnt/beta-catenin signaling occurs in certain cancers from mutation of components of the pathway and from activating growth factor receptors, including RON and MET. The resulting accumulation of cytoplasmic and nuclear beta-catenin interacts with the Tcf/LEF transcription factors to induce target genes. The IkappaB kinase complex (IKK) that phosphorylates IkappaB contains IKKalpha, IKKbeta, and IKKgamma. Here we show that the cyclin D1 gene functions as a point of convergence between the Wnt/beta-catenin and IkappaB pathways in mitogenic signaling. Mitogenic induction of G(1)-S phase progression and cyclin D1 expression was PI3K dependent, and cyclin D1(-/-) cells showed reduced PI3K-dependent S-phase entry. PI3K-dependent induction of cyclin D1 was blocked by inhibitors of PI3K/Akt/IkappaB/IKKalpha or beta-catenin signaling. A single Tcf site in the cyclin D1 promoter was required for induction by PI3K or IKKalpha. In IKKalpha(-/-) cells, mitogen-induced DNA synthesis, and expression of Tcf-responsive genes was reduced. Reintroduction of IKKalpha restored normal mitogen induction of cyclin D1 through a Tcf site. In IKKalpha(-/-) cells, beta-catenin phosphorylation was decreased and purified IKKalpha was sufficient for phosphorylation of beta-catenin through its N-terminus in vitro. Because IKKalpha but not IKKbeta induced cyclin D1 expression through Tcf activity, these studies indicate that the relative levels of IKKalpha and IKKbeta may alter their substrate and signaling specificities to regulate mitogen-induced DNA synthesis through distinct mechanisms.
Figures
References
-
- Albanese C, et al. Activation of the cyclin D1 gene by the E1A-associated protein p300 through AP-1 inhibits cellular apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:34186–34195. - PubMed
-
- Albanese C, Johnson J, Watanabe G, Eklund N, Vu D, Arnold A, Pestell RG. Transforming p21ras mutants and c-Ets-2 activate the cyclin D1 promoter through distinguishable regions. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:23589–23597. - PubMed
-
- Amanatullah D, Zafonte B, Albanese C, Fu M-F, Messiers C, Hassell J, Pestell RG. Ras regulation of cyclin D1 promoter. Methods Enzymol. 2001;332:116–127. - PubMed
-
- Ashton AW, Watanabe G, Albanese C, Harrington EO, Ware JA, Pestell RG. Protein kinase Cδ inhibition of S-phase transition in capillary endothelial cells involves the cyclin dependant kinase inhibitor p27Kip1. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:20805–20811. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

