Nup98 localizes to both nuclear and cytoplasmic sides of the nuclear pore and binds to two distinct nucleoporin subcomplexes
- PMID: 12589057
- PMCID: PMC149995
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-09-0582
Nup98 localizes to both nuclear and cytoplasmic sides of the nuclear pore and binds to two distinct nucleoporin subcomplexes
Abstract
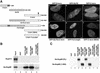
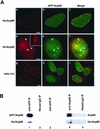
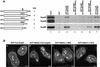
The vertebrate nuclear pore is an enormous structure that spans the double membrane of the nuclear envelope. In yeast, most nucleoporins are found symmetrically on both the nuclear and cytoplasmic sides of the structure. However, in vertebrates most nucleoporins have been localized exclusively to one side of the nuclear pore. Herein, we show, by immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy, that Nup98 is found on both sides of the pore complex. Additionally, we find that the pore-targeting domain of Nup98 interacts directly with the cytoplasmic nucleoporin Nup88, a component of the Nup214, Nup88, Nup62 subcomplex. Nup98 was previously described to interact with the nuclear-oriented Nup160, 133, 107, 96 complex through direct binding to Nup96. Interestingly, the same site within Nup98 is involved in binding to both Nup88 and Nup96. Autoproteolytic cleavage of the Nup98 C terminus is required for both of these binding interactions. When cleavage is blocked by a point mutation, a minimal eight amino acids downstream of the cleavage site is sufficient to prevent most binding to either Nup96 or Nup88. Thus, Nup98 interacts with both faces of the nuclear pore, a localization in keeping with its previously described nucleocytoplasmic shuttling activity.
Figures


References
-
- Allen TD, Cronshaw JM, Bagley S, Kiseleva E, Goldberg MW. The nuclear pore complex: mediator of translocation between nucleus and cytoplasm. J Cell Sci. 2000;113:1651–1659. - PubMed
-
- Bailer SM, Balduf C, Katahira J, Podtelejnikov A, Rollenhagen C, Mann M, Pante N, Hurt E. Nup116p associates with the Nup82p-Nsp1p-Nup159p nucleoporin complex. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:23540–23548. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

