Identification of a novel leucine-rich repeat protein as a component of flagellar radial spoke in the Ascidian Ciona intestinalis
- PMID: 12589069
- PMCID: PMC150007
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.02-06-0089
Identification of a novel leucine-rich repeat protein as a component of flagellar radial spoke in the Ascidian Ciona intestinalis
Abstract
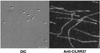
Axonemes are highly organized microtubule-based structures conserved in many eukaryotes. In an attempt to study axonemes by a proteomics approach, we selectively cloned cDNAs of axonemal proteins by immunoscreening the testis cDNA library from the ascidian Ciona intestinalis by using an antiserum against whole axonemes. We report here a 37-kDa protein of which cDNA occurred most frequently among total positive clones. This protein, named LRR37, belongs to the class of SDS22+ leucine-rich repeat (LRR) family. LRR37 is different from the LRR outer arm dynein light chain reported in Chlamydomonas and sea urchin flagella, and thus represents a novel axonemal LRR protein. Immunoelectron microscopy by using a polyclonal antibody against LRR37 showed that it is localized on the tip of the radial spoke, most likely on the spoke head. The LRR37 protein in fact seems to form a complex together with radial spoke protein 3 in a KI extract of the axonemes. These results suggest that LRR37 is a component of the radial spoke head and is involved in the interaction with other radial spoke components or proteins in the central pair projection.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Molecular characterization of radial spoke subcomplex containing radial spoke protein 3 and heat shock protein 40 in sperm flagella of the ascidian Ciona intestinalis.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Feb;16(2):626-36. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-09-0784. Epub 2004 Nov 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15563603 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic characterization of sperm radial spokes identifies a novel spoke protein with an ubiquitin domain.FEBS Lett. 2009 Jul 7;583(13):2201-7. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.06.016. Epub 2009 Jun 13. FEBS Lett. 2009. PMID: 19527718
-
Molecular basis of sperm flagellar axonemes: structural and evolutionary aspects.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Apr;1101:506-26. doi: 10.1196/annals.1389.017. Epub 2007 Mar 15. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 17363437 Review.
-
Molecular characterization of Ciona sperm outer arm dynein reveals multiple components related to outer arm docking complex protein 2.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2006 Oct;63(10):591-603. doi: 10.1002/cm.20146. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2006. PMID: 16847897
-
Molecular characterization of axonemal proteins and signaling molecules responsible for chemoattractant-induced sperm activation in Ciona intestinalis.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2008 Mar;65(3):249-67. doi: 10.1002/cm.20258. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2008. PMID: 18189282
Cited by
-
Calcium sensors of ciliary outer arm dynein: functions and phylogenetic considerations for eukaryotic evolution.Cilia. 2015 Apr 30;4:6. doi: 10.1186/s13630-015-0015-z. eCollection 2015. Cilia. 2015. PMID: 25932323 Free PMC article.
-
Dimeric novel HSP40 is incorporated into the radial spoke complex during the assembly process in flagella.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Feb;16(2):637-48. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-09-0787. Epub 2004 Nov 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15563613 Free PMC article.
-
The radial spokes and central apparatus: mechano-chemical transducers that regulate flagellar motility.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2004 Jan;57(1):8-17. doi: 10.1002/cm.10155. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2004. PMID: 14648553 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Heterogeneity of radial spoke components in Tetrahymena cilia.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025 Aug 31;82(1):329. doi: 10.1007/s00018-025-05871-x. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40886204 Free PMC article.
-
Radial spoke proteins of Chlamydomonas flagella.J Cell Sci. 2006 Mar 15;119(Pt 6):1165-74. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02811. Epub 2006 Feb 28. J Cell Sci. 2006. PMID: 16507594 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ansari-Lari MA, et al. Comparative sequence analysis of a gene-rich cluster at human chromosome 12p13 and its syntenic region in mouse chromosome 6. Genome Res. 1998;8:29–40. - PubMed
-
- Benashski SE, Patel-King RS, King SM. Light chain 1 from the Chlamydomonas outer dynein arm is a leucine-rich repeat associated with the motor domain of the γ heavy chain. Biochemistry. 1999;38:7253–7264. - PubMed
-
- Blouin JL, et al. Primary ciliary dyskinesia. a genome-wide linkage analysis reveals extensive locus heterogeneity. Eur J Hum Genet. 2000;8:109–118. - PubMed
-
- Buchanan SG, Gay NJ. Structural and functional diversity in the leucine-rich repeat family of proteins. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1996;65:1–44. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhry P, Creagh S, Yu N, Brokaw CJ. Multiple protein kinase activities required for activation of sperm flagellar motility. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1995;32:65–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

