Complex regulation of the Bacillus subtilis aconitase gene
- PMID: 12591885
- PMCID: PMC148081
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.5.1672-1680.2003
Complex regulation of the Bacillus subtilis aconitase gene
Abstract
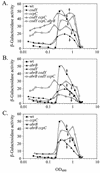
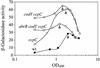
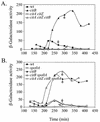
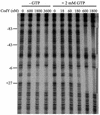
The roles of the CcpC, CodY, and AbrB proteins in regulation of the Bacillus subtilis aconitase (citB) gene were found to be distinct and to vary with the conditions and phase of growth. CcpC, a citrate-inhibited repressor that is the primary factor regulating citB expression in minimal-glucose-glutamine medium, also contributed to repression of citB during exponential-phase growth in broth medium. A null mutation in codY had no effect on citB expression during growth in minimal medium even when combined with ccpC and abrB mutations. However, a codY mutation slightly relieved repression during exponential growth in broth medium and completely derepressed citB expression when combined with a ccpC mutation. An abrB mutation led to decreased expression of citB during stationary phase in both broth and minimal medium. All three proteins bound in vitro to specific and partially overlapping sites within the citB regulatory region. Interaction of CcpC and CodY with the citB promoter region was partially competitive.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CcpC, a novel regulator of the LysR family required for glucose repression of the citB gene in Bacillus subtilis.J Mol Biol. 2000 Jan 28;295(4):865-78. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3420. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10656796
-
CcpC-dependent regulation of citB and lmo0847 in Listeria monocytogenes.J Bacteriol. 2006 Jan;188(1):179-90. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.1.179-190.2006. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16352834 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of citB expression in Bacillus subtilis: integration of multiple metabolic signals in the citrate pool and by the general nitrogen regulatory system.Arch Microbiol. 2006 Mar;185(2):136-46. doi: 10.1007/s00203-005-0078-0. Epub 2006 Jan 5. Arch Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16395550
-
Transition-state regulators: sentinels of Bacillus subtilis post-exponential gene expression.Mol Microbiol. 1993 Feb;7(3):337-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01125.x. Mol Microbiol. 1993. PMID: 8459762 Review.
-
CodY, a master integrator of metabolism and virulence in Gram-positive bacteria.Curr Genet. 2017 Jun;63(3):417-425. doi: 10.1007/s00294-016-0656-5. Epub 2016 Oct 15. Curr Genet. 2017. PMID: 27744611 Review.
Cited by
-
Antirepression as a second mechanism of transcriptional activation by a minor groove binding protein.Mol Microbiol. 2007 Apr;64(2):368-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05662.x. Mol Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17493123 Free PMC article.
-
Hierarchical expression of genes controlled by the Bacillus subtilis global regulatory protein CodY.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jun 3;111(22):8227-32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1321308111. Epub 2014 May 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24843172 Free PMC article.
-
Systems Level Analyses Reveal Multiple Regulatory Activities of CodY Controlling Metabolism, Motility and Virulence in Listeria monocytogenes.PLoS Genet. 2016 Feb 19;12(2):e1005870. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005870. eCollection 2016 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 26895237 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of Bacillus subtilis CodY with GTP.J Bacteriol. 2008 Feb;190(3):798-806. doi: 10.1128/JB.01115-07. Epub 2007 Nov 9. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 17993518 Free PMC article.
-
Two roles for aconitase in the regulation of tricarboxylic acid branch gene expression in Bacillus subtilis.J Bacteriol. 2013 Apr;195(7):1525-37. doi: 10.1128/JB.01690-12. Epub 2013 Jan 25. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23354745 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ansari, A. Z., J. E. Bradner, and T. V. O'Halloran. 1995. DNA-bend modulation in a repressor-to-activator switching mechanism. Nature 374:371-375. - PubMed
-
- Burbulys, D., K. A. Trach, and J. A. Hoch. 1991. Initiation of sporulation in B. subtilis is controlled by a multicomponent phosphorelay. Cell 64:545-552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

