Control of immune responses by naturally arising CD4+ regulatory T cells that express toll-like receptors
- PMID: 12591898
- PMCID: PMC2193860
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20030012
Control of immune responses by naturally arising CD4+ regulatory T cells that express toll-like receptors
Figures
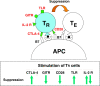
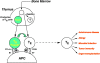
Comment on
-
Regulatory T cells selectively express toll-like receptors and are activated by lipopolysaccharide.J Exp Med. 2003 Feb 17;197(4):403-11. doi: 10.1084/jem.20021633. J Exp Med. 2003. PMID: 12591899 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cohn, M. 1994. The wisdom of hindsight. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 12:1–62. - PubMed
-
- Medzhitov, R., and C.A. Janeway, Jr. 2002. Decoding the patterns of self and nonself by the innate immune system. Science. 296:298–300. - PubMed
-
- Matzinger, P. 2002. The danger model: a renewed sense of self. Science. 296:301–305. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi, S., N. Sakaguchi, J. Shimizu, S. Yamazaki, T. Sakihama, M. Itoh, Y. Kuniyasu, T. Nomura, M. Toda, and T. Takahashi. 2001. Immunologic tolerance maintained by CD25+ CD4+ regulatory T cells: their common role in controlling autoimmunity, tumor immunity, and transplantation tolerance. Immunol. Rev. 182:18–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

