Molecular mechanism of recruitment of TFIIF- associating RNA polymerase C-terminal domain phosphatase (FCP1) by transcription factor IIF
- PMID: 12591941
- PMCID: PMC151334
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.262798199
Molecular mechanism of recruitment of TFIIF- associating RNA polymerase C-terminal domain phosphatase (FCP1) by transcription factor IIF
Abstract
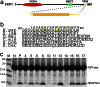
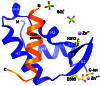
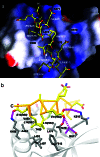
After mRNA transcription termination in eukaryotes, the hyperphosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II (pol II0) must be recycled by TFIIF-associating C-terminal domain phosphatase (FCP1), the phosphatase responsible for dephosphorylating the C-terminal domain of the largest polymerase subunit. Transcription factor (TF)-IIF stimulates the activity of FCP1, and the RNA polymerase II-associating protein 74 subunit of TFIIF forms a complex with FCP1 in both human and yeast. Here, we report a cocrystal structure of the winged-helix domain of human RNA polymerase II-associating protein 74 bound to the alpha-helical C terminus of human FCP1 (residues 944-961). These results illustrate the molecular mechanism by which TFIIF efficiently recruits FCP1 to the pol II transcription machinery for recycling of the polymerase.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Native-based simulations of the binding interaction between RAP74 and the disordered FCP1 peptide.J Phys Chem B. 2013 Mar 21;117(11):3074-85. doi: 10.1021/jp310293b. Epub 2013 Mar 12. J Phys Chem B. 2013. PMID: 23387368
-
NMR structure of a complex formed by the carboxyl-terminal domain of human RAP74 and a phosphorylated peptide from the central domain of the FCP1 phosphatase.Biochemistry. 2009 Mar 10;48(9):1964-74. doi: 10.1021/bi801549m. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19215094
-
Enhanced binding of RNAP II CTD phosphatase FCP1 to RAP74 following CK2 phosphorylation.Biochemistry. 2005 Mar 1;44(8):2732-45. doi: 10.1021/bi047958h. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 15723518
-
The histone fold is a key structural motif of transcription factor TFIID.Trends Biochem Sci. 2001 Apr;26(4):250-7. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)01741-2. Trends Biochem Sci. 2001. PMID: 11295558 Review.
-
Protein phosphatases--a phylogenetic perspective.Chem Rev. 2001 Aug;101(8):2291-312. doi: 10.1021/cr0002543. Chem Rev. 2001. PMID: 11749374 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Structure and mechanism of the RNA polymerase II transcription machinery.Genes Dev. 2020 Apr 1;34(7-8):465-488. doi: 10.1101/gad.335679.119. Genes Dev. 2020. PMID: 32238450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Position of the general transcription factor TFIIF within the RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex.EMBO J. 2010 Feb 17;29(4):706-16. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.386. Epub 2009 Dec 24. EMBO J. 2010. PMID: 20033062 Free PMC article.
-
NMR structure of a complex containing the TFIIF subunit RAP74 and the RNA polymerase II carboxyl-terminal domain phosphatase FCP1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 May 13;100(10):5688-93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1031524100. Epub 2003 May 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12732728 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin-Dependent Kinases (CDK) and Their Role in Diseases Development-Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 13;22(6):2935. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062935. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33805800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A glutamine-based single α-helix scaffold to target globular proteins.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 18;13(1):7073. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34793-6. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36400768 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

