Probing the kinesin reaction cycle with a 2D optical force clamp
- PMID: 12591957
- PMCID: PMC151344
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0436709100
Probing the kinesin reaction cycle with a 2D optical force clamp
Abstract
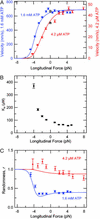
With every step it takes, the kinesin motor undergoes a mechanochemical reaction cycle that includes the hydrolysis of one ATP molecule, ADPP(i) release, plus an unknown number of additional transitions. Kinesin velocity depends on both the magnitude and the direction of the applied load. Using specialized apparatus, we subjected single kinesin molecules to forces in differing directions. Sideways and forward loads up to 8 pN exert only a weak effect, whereas comparable forces applied in the backward direction lead to stall. This strong directional bias suggests that the primary working stroke is closely aligned with the microtubule axis. Sideways loads slow the motor asymmetrically, but only at higher ATP levels, revealing the presence of additional, load-dependent transitions late in the cycle. Fluctuation analysis shows that the cycle contains at least four transitions, and confirms that hydrolysis remains tightly coupled to stepping. Together, our findings pose challenges for models of kinesin motion.
Figures



References
-
- Schnitzer M J, Visscher K, Block S M. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:718–723. - PubMed
-
- deCastro M J, Fondecave R M, Clarke L A, Schmidt C F, Stewart R J. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:724–729. - PubMed
-
- Rice S, Lin A W, Safer D, Hart C L, Naber N, Carragher B O, Cain S M, Pechatnikova E, Wilson-Kubalek E M, Whittaker M, et al. Nature. 1999;402:778–784. - PubMed
-
- Svoboda K, Schmidt C F, Schnapp B J, Block S M. Nature. 1993;365:721–727. - PubMed
-
- Sindelar C V, Budny M J, Rice S, Naber N, Fletterick R, Cooke R. Nat Struct Biol. 2002;9:844–848. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

