Backbone dynamics of the human MIA protein studied by (15)N NMR relaxation: implications for extended interactions of SH3 domains
- PMID: 12592021
- PMCID: PMC2312446
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.0222603
Backbone dynamics of the human MIA protein studied by (15)N NMR relaxation: implications for extended interactions of SH3 domains
Abstract
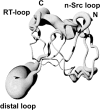
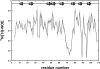
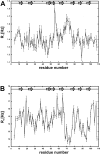
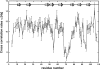
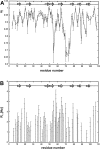
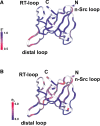
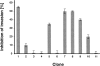
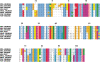
The melanoma inhibitory activity (MIA) protein is a clinically valuable marker in patients with malignant melanoma as enhanced values diagnose metastatic melanoma stages III and IV. Here, we report the backbone dynamics of human MIA studied by (15)N NMR relaxation experiments. The folded core of human MIA is found to be rigid, but several loops connecting beta-sheets, such as the RT-loop for example, display increased mobility on picosecond to nanosecond time scales. One of the most important dynamic features is the pronounced flexibility of the distal loop, comprising residues Asp 68 to Ala 75, where motions on time scales up to milliseconds occur. Further, significant exchange contributions are observed for residues of the canonical binding site of SH3 domains including the RT-loop, the n-Src loop, for the loop comprising residues 13 to 19, which we refer to as the"disulfide loop", in part for the distal loop, and the carboxyl terminus of human MIA. The functional importance of this dynamic behavior is discussed with respect to the biological activity of several point mutations of human MIA. The results of this study suggest that the MIA protein and the recently identified highly homologous fibrocyte-derived protein (FDP)/MIA-like (MIAL) constitute a new family of secreted proteins that adopt an SH3 domain-like fold in solution with expanded ligand interactions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The extracellular human melanoma inhibitory activity (MIA) protein adopts an SH3 domain-like fold.EMBO J. 2001 Feb 1;20(3):340-9. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.3.340. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11157741 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular SH3 domain containing proteins--features of a new protein family.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2008 Jun;9(3):221-6. doi: 10.2174/138920308784534014. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2008. PMID: 18537677 Review.
-
NMR-based Drug Development and Improvement Against Malignant Melanoma - Implications for the MIA Protein Family.Curr Med Chem. 2017;24(17):1788-1796. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170608104347. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28595551 Review.
-
Solution structure and dynamics of melanoma inhibitory activity protein.J Biomol NMR. 2002 Mar;22(3):211-23. doi: 10.1023/a:1014961408029. J Biomol NMR. 2002. PMID: 11991352
-
Expression, function and clinical relevance of MIA (melanoma inhibitory activity).Histol Histopathol. 2002 Jan;17(1):289-300. doi: 10.14670/HH-17.289. Histol Histopathol. 2002. PMID: 11813878 Review.
Cited by
-
Uncovering the pathogenesis and identifying novel targets of pancreatic cancer using bioinformatics approach.Mol Biol Rep. 2014 Jul;41(7):4697-704. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3340-1. Epub 2014 Apr 12. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. Retraction in: Mol Biol Rep. 2015 Oct;42(10):1463. doi: 10.1007/s11033-015-3895-5. PMID: 24728565 Retracted.
-
Ras homolog enriched in brain (Rheb) enhances apoptotic signaling.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 29;285(44):33979-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.095968. Epub 2010 Aug 4. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20685651 Free PMC article.
-
Human melanoma inhibitory protein binds to the FN12-14 Hep II domain of fibronectin.Biointerphases. 2017 May 31;12(2):02D415. doi: 10.1116/1.4984008. Biointerphases. 2017. PMID: 28565914 Free PMC article.
-
Backbone dynamics in an intramolecular prolylpeptide-SH3 complex from the diphtheria toxin repressor, DtxR.J Mol Biol. 2007 Dec 7;374(4):977-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.09.063. Epub 2007 Oct 31. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17976643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albini, A., Iwamoto, Y., Kleinmann, H.K., Martin, G.R., Aaronson, S.A., Kozlowski, J.M., and McEwan, R.N. 1987. A rapid in vitro assay for quantitating the invasive potential of tumor cells. Cancer Res. 47 3239–3245. - PubMed
-
- Appel, R.D., Bairoch, A., and Hochstrasser, D.F. 1994. A new generation of information retrieval tools for biologists: The example of the ExPASy WWW server. Trends Biochem. Sci. 19 258–260. - PubMed
-
- Blesch, A., Bosserhoff, A.K., Apfel, R., Behl, C., Hessdoerfer, B., Schmitt, A., Jachimczak, P., Lottspeich, F., Buettner, R., and Bogdahn, U. 1994. Cloning of a novel malignant melanoma-derived growth regulatory protein, MIA. Cancer Res 54 5695–5701. - PubMed
-
- Bogdahn, U., Apfel, R., Hahn, M., Gerlach, M., Behl, C., Hoppe, J., and Martin, R. 1989. Autocrine tumor cell growth inhibiting activities from human malignant melanoma. Cancer Res. 49 5358–5363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

