Acute encephalopathy associated with influenza A virus infection
- PMID: 12594636
- PMCID: PMC7199495
- DOI: 10.1086/367623
Acute encephalopathy associated with influenza A virus infection
Abstract
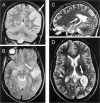
Twenty-one patients aged 4-78 years with influenza A virus-associated acute encephalopathy were studied. Influenza A virus could be detected only in a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) specimen obtained from 1 of 18 patients, despite the use of a highly sensitive polymerase chain reaction assay. Six patients experienced influenzal encephalopathy during the course of respiratory illness. Five of these patients had hypoprothrombinemia and 4 had increased serum creatinine levels, indicating hepatic and/or renal dysfunction. Fourteen patients experienced postinfluenzal encephalopathy <or=3 weeks after resolution of acute respiratory symptoms. In 6 patients, focal areas of high signal intensity were visible on T2-weighted magnetic resonance images of the brain. Adenovirus DNA was detected in CSF specimens obtained from 4 (36%) of 11 patients with postinfluenzal encephalopathy. Thus, influenzal encephalopathy is frequently associated with metabolic disorders, whereas postinfluenzal encephalopathy appears to have different possible etiologies.
Figures

References
-
- Wright PF, Webster RG. Orthomyxoviruses. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Field's virology. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Raven; 2001. pp. 1533–79.
-
- Mellman WJ. Influenza encephalitis. J Pediatr. 1958;1:292–7. - PubMed
-
- Flewett TH, Hoult JG. Influenza encephalopathy and postinfluenza encephalitis. Lancet. 1958;2:11–5. - PubMed
-
- Nicholson KG, Webster RG, Hay AJ. Textbook of influenza. London: Blackwell Science; 1998.
-
- Morishima T, Togashi T, Yokota S, et al. Encephalitis and encephalopathy associated with an influenza epidemic in Japan. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;35:512–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

