The Afa/Dr adhesins of diffusely adhering Escherichia coli stimulate interleukin-8 secretion, activate mitogen-activated protein kinases, and promote polymorphonuclear transepithelial migration in T84 polarized epithelial cells
- PMID: 12595416
- PMCID: PMC148852
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.3.1068-1074.2003
The Afa/Dr adhesins of diffusely adhering Escherichia coli stimulate interleukin-8 secretion, activate mitogen-activated protein kinases, and promote polymorphonuclear transepithelial migration in T84 polarized epithelial cells
Abstract
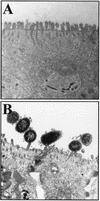
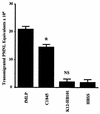
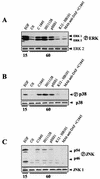
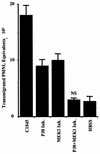
Afa/Dr diffusely adhering Escherichia coli (Afa/Dr DAEC) strains cause symptomatic urinary tract and intestinal infections. The proinflammatory effects of Afa/Dr DAEC strains in vitro have been not investigated to date. In the present study, we used confluent polarized monolayers of intestinal cell line T84 to evaluate the consequences of epithelial infection by Afa/Dr DAEC strains in terms of proinflammatory response. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMNL) migration across the epithelial barrier was induced after incubation of the T84 monolayers with the wild-type Afa/Dr DAEC strain C1845 harboring the fimbrial F1845 adhesin and strain IH11128 harboring the Dr hemagglutinin, and the E. coli laboratory strain HB101 was transformed with the pSSS1 plasmid, producing Afa/Dr F1845 adhesin. PMNL migrations were correlated with a basolateral secretion of interleukin-8 by T84 cells and were abolished after incubation of epithelial cells with an anti-decay accelerating factor (DAF) antibody that recognized the short consensus repeat 3 domain of DAF (monoclonal antibody 1H4). Moreover, Afa/Dr DAEC strains induced tyrosine phosphorylation of several T84 proteins and activated the mitogen-activated protein kinases (ERK1/2 mitogen-activated protein, P38, and Jun-C kinases). These data demonstrated for the first time that, in vitro, Afa/Dr DAEC strains exert a proinflammatory signal in intestinal epithelial cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Afa/Dr diffusely adhering Escherichia coli infection in T84 cell monolayers induces increased neutrophil transepithelial migration, which in turn promotes cytokine-dependent upregulation of decay-accelerating factor (CD55), the receptor for Afa/Dr adhesins.Infect Immun. 2003 Apr;71(4):1774-83. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.4.1774-1783.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12654791 Free PMC article.
-
Recruitment of CD55 and CD66e brush border-associated glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins by members of the Afa/Dr diffusely adhering family of Escherichia coli that infect the human polarized intestinal Caco-2/TC7 cells.Infect Immun. 2000 Jun;68(6):3554-63. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.6.3554-3563.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10816511 Free PMC article.
-
Increased rate of apoptosis and diminished phagocytic ability of human neutrophils infected with Afa/Dr diffusely adhering Escherichia coli strains.Infect Immun. 2004 Oct;72(10):5741-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.10.5741-5749.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15385473 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of Afa/Dr diffusely adhering Escherichia coli.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2005 Apr;18(2):264-92. doi: 10.1128/CMR.18.2.264-292.2005. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2005. PMID: 15831825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenesis of human diffusely adhering Escherichia coli expressing Afa/Dr adhesins (Afa/Dr DAEC): current insights and future challenges.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2014 Oct;27(4):823-69. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00036-14. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2014. PMID: 25278576 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microbes-induced EMT at the crossroad of inflammation and cancer.Gut Microbes. 2012 May-Jun;3(3):176-85. doi: 10.4161/gmic.20288. Epub 2012 May 1. Gut Microbes. 2012. PMID: 22572828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Afa/Dr-expressing, diffusely adhering Escherichia coli strain C1845 triggers F1845 fimbria-dependent phosphatidylserine externalization on neutrophil-like differentiated PLB-985 cells through an apoptosis-independent mechanism.Infect Immun. 2010 Jul;78(7):2974-83. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01354-09. Epub 2010 Apr 19. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20404079 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of human enterovirulent bacteria: lessons from cultured, fully differentiated human colon cancer cell lines.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2013 Sep;77(3):380-439. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00064-12. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2013. PMID: 24006470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pili Assembled by the Chaperone/Usher Pathway in Escherichia coli and Salmonella.EcoSal Plus. 2018 Mar;8(1):10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0007-2017. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0007-2017. EcoSal Plus. 2018. PMID: 29536829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Afa/Dr diffusely adhering Escherichia coli strain C1845 induces neutrophil extracellular traps that kill bacteria and damage human enterocyte-like cells.Infect Immun. 2012 May;80(5):1891-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00050-12. Epub 2012 Feb 27. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 22371374 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baqui, A. H., R. B. Sack, R. E. Black, K. Haider, A. Hossain, A. R. Alim, M. Yunus, H. R. Chowdhury, and A. K. Siddique. 1992. Enteropathogens associated with acute and persistent diarrhea in Bangladeshi children less than 5 years of age. J. Infect. Dis. 166:792-796. - PubMed
-
- Bernet-Camard, M. F., M. H. Coconnier, S. Hudault, and A. L. Servin. 1996. Pathogenicity of the diffusely adhering strain Escherichia coli C1845: F1845 adhesin-decay accelerating factor interaction, brush border microvillus injury, and actin disassembly in cultured human intestinal epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 64:1918-1928. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bocciardi, R., B. Mograbi, B. Pasini, M. G. Borrello, M. A. Pierotti, I. Bourget, S. Fischer, G. Romeo, and B. Rossi. 1997. The multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B point mutation switches the specificity of the Ret tyrosine kinase towards cellular substrates that are susceptible to interact with Crk and Nck. Oncogene 15:2257-2265. - PubMed
-
- Branka, J. E., G. Vallette, A. Jarry, C. Bou-Hanna, P. Lemarre, P. N. Van, and C. L. Laboisse. 1997. Early functional effects of Clostridium difficile toxin A on human colonocytes. Gastroenterology 112:1887-1894. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

