Rho GTPase is activated by cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 in peripheral blood T lymphocytes: potential cytotoxicity for intestinal epithelial cells
- PMID: 12595428
- PMCID: PMC148851
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.3.1161-1169.2003
Rho GTPase is activated by cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 in peripheral blood T lymphocytes: potential cytotoxicity for intestinal epithelial cells
Abstract
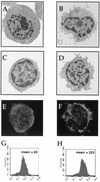
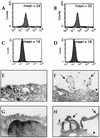
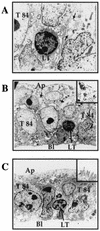
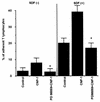
Some strains of Escherichia coli related to acute cystitis or colitis produce a toxin named cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 (CNF-1). CNF-1 mediates its effects on epithelial cells or phagocytes via the permanent activation of small GTP-binding proteins, caused by the toxin-induced deamidation of Glu(63) of p21 Rho. The behavior of peripheral blood T lymphocytes during the acute phase of bacterial colitis has been poorly investigated. Our study was conducted to test whether (i) peripheral blood T lymphocytes can be activated by CNF-1 and (ii) CNF-1-activated T lymphocytes are cytotoxic against intestinal epithelial cells. Activation of T lymphocytes by CNF-1 was assessed by electrophoresis, flow cytometry, confocal microscopy, and electron microscopy studies. Assays for migration and adherence of CNF-1-treated T lymphocytes were performed in Transwell chambers with T84 intestinal epithelial cells grown on polycarbonate semipermeable filters. CNF-1 induced a decrease in the electrophoretic mobility of the GTP-binding protein Rho in treated T lymphocytes. CNF-1 provoked an increase in the content of actin stress fibers and pseudopodia in T lymphocytes. Several adherence molecules were clustered into cytoplasmic projections in CNF-1-treated T lymphocytes and adherence of such lymphocytes on the basolateral pole of T84 was increased, resulting in cytotoxicity toward epithelial cells. Such enhanced adherence in response to CNF-1 was dependent on p42-44(MAP) kinase activation of T lymphocytes. Taken together, these results suggest that CNF-1, by acting on T lymphocytes, may increase in an important fashion the virulence of certain strains of E. coli against the intestinal epithelia.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Constitutive activation of Rho proteins by CNF-1 influences tight junction structure and epithelial barrier function.J Cell Sci. 2003 Feb 15;116(Pt 4):725-42. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00300. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 12538773
-
Escherichia coli cytotoxic necrotizing factor-1 (CNF-1) increases the adherence to epithelia and the oxidative burst of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes but decreases bacteria phagocytosis.J Leukoc Biol. 2000 Oct;68(4):522-8. J Leukoc Biol. 2000. PMID: 11037974
-
Differential role of Rho GTPases in intestinal epithelial barrier regulation in vitro.J Cell Physiol. 2011 May;226(5):1196-203. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22446. J Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 20945370
-
Cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 from Escherichia coli: a toxin with a new intracellular activity for eukaryotic cells.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 1998;43(3):285-9. doi: 10.1007/BF02818614. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 1998. PMID: 9717256 Review.
-
The cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 (CNF1) from Escherichia coli.Toxicon. 2001 Nov;39(11):1673-80. doi: 10.1016/s0041-0101(01)00154-4. Toxicon. 2001. PMID: 11595630 Review.
Cited by
-
Escherichia coli cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 inhibits intestinal epithelial wound healing in vitro after mechanical injury.Infect Immun. 2004 Oct;72(10):5733-40. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.10.5733-5740.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15385472 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the Escherichia coli Bacterial Toxin Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 on Different Human and Animal Cells: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 22;22(22):12610. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212610. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830494 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory properties of CNF1 toxin from E. coli: implications for colorectal carcinogenesis.Am J Cancer Res. 2022 Feb 15;12(2):651-660. eCollection 2022. Am J Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35261793 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Balazovich, K. J., R. Fernandez, V. Hinkovska-Galcheva, S. J. Suchard, and L. A. Boxer. 1996. Transforming growth factor-beta1 stimulates degranulation and oxidant release by adherent human neutrophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 60:772-777. - PubMed
-
- Beagley, K. W., and A. J. Husband. 1998. Intraepithelial lymphocytes: origins, distribution, and function. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 18:237-254. - PubMed
-
- Boquet, P. 1998. Cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 from Escherichia coli: a toxin with a new intracellular activity for eukaryotic cells. Folia Micobiol. 43:285-289. - PubMed
-
- Boquet, P., P. Munro, C. Fiorentini, and I. Just. 1998. Toxins from anaerobic bacteria: specificity and molecular mechanisms of action. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 1:66-74. - PubMed
-
- Boquet, P., G. Tran Van Nieugh, and P. Sansonetti. 1999. Cell regulation and Rho GTP-binding proteins?, p. 183-199. In P. Jeanteur (ed.). Small Rho GTPases and microbial pathogenicity. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

