Role of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway and kappaB cis-regulatory elements on the IRF-1 and iNOS promoter regions in mycobacterial lipoarabinomannan induction of nitric oxide
- PMID: 12595462
- PMCID: PMC148845
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.3.1442-1452.2003
Role of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway and kappaB cis-regulatory elements on the IRF-1 and iNOS promoter regions in mycobacterial lipoarabinomannan induction of nitric oxide
Abstract
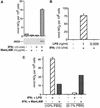
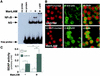
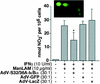
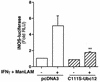
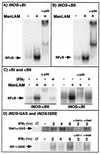
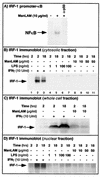
Nitric oxide (NO(.)) produced by inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) is an important host defense molecule against Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mononuclear phagocytes. The objective of this study was to determine the role of the IkappaBalpha kinase-nuclear factor kappaB (IKK-NF-kappaB) signaling pathway in the induction of iNOS and NO(.) by a mycobacterial cell wall lipoglycan known as mannose-capped lipoarabinomannan (ManLAM) in mouse macrophages costimulated with gamma interferon (IFN-gamma). NF-kappaB was activated by ManLAM as shown by electrophoretic mobility shift assay, by immunofluorescence of translocated NF-kappaB in intact cells, and by a reporter gene driven by four NF-kappaB-binding elements. Transduction of an IkappaBalpha mutant (Ser32/36Ala) significantly inhibited NO(.) expression induced by IFN-gamma plus ManLAM. An activated SCF complex, a heterotetramer (Skp1, Cul-1, beta-TrCP [F-box protein], and ROC1) involved with ubiquitination, is also required for iNOS-NO(.) induction. Two NF-kappaB-binding sites (kappaBI and kappaBII) present on the 5'-flanking region of the iNOS promoter bound ManLAM-induced NF-kappaB similarly. By use of reporter constructs in which one or both sites are mutated, both NF-kappaB-binding positions were essential in iNOS induction by IFN-gamma plus ManLAM. IFN-gamma-induced activation of the IRF-1 transcriptional complex is a necessary component in host defense against tuberculosis. Although the 5'-flanking region of the IRF-1 promoter contains an NF-kappaB-binding site and ManLAM-induced NF-kappaB also binds to this site, ManLAM was unable to induce IRF-1 expression. The influence of mitogen-activated protein kinases on IFN-gamma plus ManLAM induction of iNOS-NO(.) is not due to any effects on ManLAM induction of NF-kappaB.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase-NO* by lipoarabinomannan of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is mediated by MEK1-ERK, MKK7-JNK, and NF-kappaB signaling pathways.Infect Immun. 2001 Apr;69(4):2001-10. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.4.2001-2010.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11254551 Free PMC article.
-
Docosahexaenoic acid decreases IRF-1 mRNA and thus inhibits activation of both the IRF-E and NFkappa d response elements of the iNOS promoter.Transplantation. 2000 May 27;69(10):2131-7. doi: 10.1097/00007890-200005270-00030. Transplantation. 2000. PMID: 10852612
-
Interaction of interferon regulatory factor-1 and nuclear factor kappaB during activation of inducible nitric oxide synthase transcription.J Mol Biol. 1999 Jun 11;289(3):459-71. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.2752. J Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10356322
-
Nitric oxide and viral infection: Recent developments in antiviral therapies and platforms.Appl Mater Today. 2021 Mar;22:100887. doi: 10.1016/j.apmt.2020.100887. Epub 2020 Dec 5. Appl Mater Today. 2021. PMID: 38620577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mannose-capped lipoarabinomannan in Mycobacterium tuberculosis pathogenesis.Pathog Dis. 2018 Jun 1;76(4):fty026. doi: 10.1093/femspd/fty026. Pathog Dis. 2018. PMID: 29722821 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Allicin Alleviated LPS-Induced Mastitis via the TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 14;24(4):3805. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043805. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835218 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorative effects of berberine and selenium against paracetamol-induced hepatic toxicity in rats.Open Vet J. 2024 Jan;14(1):292-303. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2024.v14.i1.26. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Open Vet J. 2024. PMID: 38633147 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB regulates GDF-15 to suppress macrophage surveillance during early tumor development.J Clin Invest. 2017 Oct 2;127(10):3796-3809. doi: 10.1172/JCI91561. Epub 2017 Sep 11. J Clin Invest. 2017. PMID: 28891811 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying a gene signature of metastatic potential by linking pre-metastatic state to ultimate metastatic fate.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 17:2024.08.14.607813. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.14.607813. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39185156 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
The anti-inflammatory effect of melatonin on methamphetamine-induced proinflammatory mediators in human neuroblastoma dopamine SH-SY5Y cell lines.Neurotox Res. 2013 Feb;23(2):189-99. doi: 10.1007/s12640-012-9350-7. Epub 2012 Aug 18. Neurotox Res. 2013. PMID: 22903344
References
-
- Adams, L. B., M. C. Dinauer, D. E. Morgenstern, and J. L. Krahenbuhl. 1997. Comparison of the roles of reactive oxygen and nitrogen intermediates in the host response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis using transgenic mice. Tuber. Lung Dis. 78:237-246. - PubMed
-
- Alepuz, P. M., A. Jovanovic, V. Reiser, and G. Ammerer. 2001. Stress-induced MAP kinase Hog1 is part of transcription activation complexes. Mol. Cell 7:767-777. - PubMed
-
- Alpert, D., P. Schwenger, J. Han, and J. Vilcek. 1999. Cell stress and MKK6b-mediated p38 MAP kinase activation inhibit tumor necrosis factor-induced IκB phosphorylation and NF-κB activation. J. Biol. Chem. 274:22176-22183. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle, P. A. 1998. Pro-inflammatory signaling: last pieces in the NF-κB puzzle? Curr. Biol. 8:R19-R22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

