Macrophage recognition and phagocytosis of apoptotic fibroblasts is critically dependent on fibroblast-derived thrombospondin 1 and CD36
- PMID: 12598312
- PMCID: PMC1868087
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63874-6
Macrophage recognition and phagocytosis of apoptotic fibroblasts is critically dependent on fibroblast-derived thrombospondin 1 and CD36
Abstract
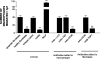
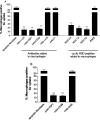
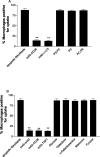
The induction of fibroblast apoptosis and their clearance by phagocytes is essential for normal wound healing and prevention of scarring. However, little is known about the clearance of apoptotic fibroblasts and whether apoptotic cells are active participants in the recruitment and activation of phagocytes. In this study, we provide the first evidence that apoptotic fibroblasts actively release increased amounts of thrombospondin (TSP1) to actively recruit macrophages. Expression of TSP1 and its receptor CD36 was increased on the surface of apoptotic fibroblasts. By chemical cross-linking and immunoprecipitation we show that TSP1 and CD36 were directly associated. This was confirmed by confocal microscopy. Blockade of either CD36 or TSP1 on apoptotic fibroblasts inhibited phagocytosis. Blockade of alpha v beta 3 integrins as well as CD36 and TSP1 on macrophages inhibited phagocytosis. In contrast, phosphatidylserine or lectins were not involved. These findings suggest that apoptotic fibroblasts release TSP1 as a signal to recruit macrophages while the up-regulated expression of the CD36/TSP1 complex on their cell surface may form a ligand bridging the fibroblast to a complex consisting of alpha v beta 3/CD36/TSP1 on macrophages. These results establish fundamental mechanisms for the clearance of apoptotic fibroblasts and may provide insights into the processes involved in normal wound repair.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Human glomerular mesangial cell phagocytosis of apoptotic neutrophils: mediation by a novel CD36-independent vitronectin receptor/thrombospondin recognition mechanism that is uncoupled from chemokine secretion.J Immunol. 1997 May 1;158(9):4389-97. J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9127003
-
Human monocyte-derived macrophage phagocytosis of senescent eosinophils undergoing apoptosis. Mediation by alpha v beta 3/CD36/thrombospondin recognition mechanism and lack of phlogistic response.Am J Pathol. 1996 Sep;149(3):911-21. Am J Pathol. 1996. PMID: 8780395 Free PMC article.
-
CD36 is required for phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by human macrophages that use either a phosphatidylserine receptor or the vitronectin receptor (alpha v beta 3).J Immunol. 1998 Dec 1;161(11):6250-7. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9834113
-
Thrombospondin 1: a multifunctional protein implicated in the regulation of tumor growth.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2004 Mar;49(3):245-58. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2003.09.009. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2004. PMID: 15036264 Review.
-
Granulocyte apoptosis and the control of inflammation.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1994 Aug 30;345(1313):327-33. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1994.0113. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1994. PMID: 7846130 Review.
Cited by
-
Endothelial-derived thrombospondin-1 promotes macrophage recruitment and apoptotic cell clearance.J Cell Mol Med. 2010 Jul;14(7):1922-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00799.x. Epub 2009 Jun 5. J Cell Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 19508384 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Perspectives in Chronic Kidney Disease-Specific Cardiovascular Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 24;25(5):2658. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052658. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory Mechanisms Triggered by Apoptotic Cells during Their Clearance.Front Immunol. 2017 Aug 2;8:909. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00909. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28824635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thrombospondin 1 promotes tumor macrophage recruitment and enhances tumor cell cytotoxicity of differentiated U937 cells.Cancer Res. 2008 Sep 1;68(17):7090-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0643. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18757424 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis modulation as a promising target for treatment of systemic sclerosis.Int J Rheumatol. 2011;2011:495792. doi: 10.1155/2011/495792. Epub 2011 Sep 6. Int J Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21912551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lorena D, Uchio K, Costa AM, Desmouliere A: Normal scarring: importance of myofibroblasts. Wound Repair Regen 2002, 10:86-92 - PubMed
-
- Ogasawara JR, Watanabe-Fukunaga M, Adachi A, Matsuzawa T, Kasugai Y, Kitamura N, Itoh T, Suda S, Nagata S: Lethal effect of the anti-Fas antibody in mice. Nature 1993, 364:806-809 - PubMed
-
- Dini L, Autuori F, Lentini A, Oliverio S, Piacentini M: The clearance of apoptotic cells in the liver is mediated by the asialoglycoprotein receptor. FEBS Lett 1992, 296:174-178 - PubMed
-
- Schlegel R, Krahling S, Callahan MK, Williamson P: CD14 is a component of multiple recognition systems used by macrophages to phagocytose apoptotic lymphocytes. Cell Death Differ 1999, 6:583-592 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

