Stress inhibits hair growth in mice by induction of premature catagen development and deleterious perifollicular inflammatory events via neuropeptide substance P-dependent pathways
- PMID: 12598315
- PMCID: PMC1868104
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63877-1
Stress inhibits hair growth in mice by induction of premature catagen development and deleterious perifollicular inflammatory events via neuropeptide substance P-dependent pathways
Abstract
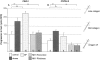
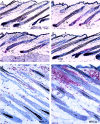
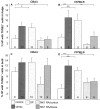
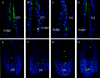
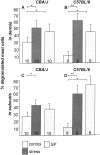
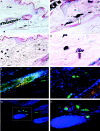
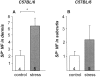
It has been much disputed whether or not stress can cause hair loss (telogen effluvium) in a clinically relevant manner. Despite the paramount psychosocial importance of hair in human society, this central, yet enigmatic and controversial problem of clinically applied stress research has not been systematically studied in appropriate animal models. We now show that psychoemotional stress indeed alters actual hair follicle (HF) cycling in vivo, ie, prematurely terminates the normal duration of active hair growth (anagen) in mice. Further, inflammatory events deleterious to the HF are present in the HF environment of stressed mice (perifollicular macrophage cluster, excessive mast cell activation). This provides the first solid pathophysiological mechanism for how stress may actually cause telogen effluvium, ie, by hair cycle manipulation and neuroimmunological events that combine to terminate anagen. Furthermore, we show that most of these hair growth-inhibitory effects of stress can be reproduced by the proteotypic stress-related neuropeptide substance P in nonstressed mice, and can be counteracted effectively by co-administration of a specific substance P receptor antagonist in stressed mice. This offers the first convincing rationale how stress-induced hair loss in men may be pharmacologically managed effectively.
Figures

Comment in
-
Stress and the hair follicle: exploring the connections.Am J Pathol. 2003 Mar;162(3):709-12. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63866-7. Am J Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12598304 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Selye H: The Physiology and Pathology of Exposure to Stress. 1950:p 727 ACTA Inc. Medical Publishers, Montreal
-
- Trepat L, Petre AJ: ‘Pelada Universal por shock emotiva.’ Semana Méd 1942, 1:65
-
- Whitlock FA: Rook A eds. Psychophysiological aspects of skin disease. Major Problems in Dermatology 1976, vol 8. Saunders, London
-
- York J, Nicholson T, Minors P, Duncan DF: Stressful life events and loss of hair among adult women, a case-control study. Psychol Rep 1998, 82:1044-1046 - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Hernandez MJ, Ruiz-Doblado S, Rodriguez-Pichardo A, Camacho F: Alopecia areata, stress and psychiatric disorders: a review. J Dermatol 1999, 26:625-662 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

