AIM inhibits apoptosis of T cells and NKT cells in Corynebacterium-induced granuloma formation in mice
- PMID: 12598318
- PMCID: PMC1868086
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63880-1
AIM inhibits apoptosis of T cells and NKT cells in Corynebacterium-induced granuloma formation in mice
Abstract
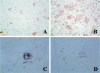
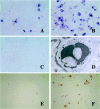
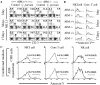
Apoptosis inhibitor expressed by macrophages (AIM) inhibits apoptosis of CD4(+)CD8(+) (CD4/CD8) double-positive thymocytes, and supports the viability of these cells on the thymic selection. However, pleiotropic functions of AIM have been suggested. In this study, heat-killed Corynebacterium parvum (C. parvum) was injected into mice carrying the homozygous mutation (AIM(-/-)) and wild-type (AIM(+/+)) mice, to investigate the role of AIM in the formation of hepatic granulomas. In AIM(-/-) mice, the size and the number of hepatic granulomas were larger, and the resorption of granulomas was more delayed than in AIM(+/+) mice. The production of interleukin-12 was more prominent in AIM(-/-) mice than in AIM(+/+) mice. In the liver of AIM(+/+) mice, expression of AIM messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) increased after C. parvum injection. In situ hybridization demonstrated that AIM mRNA was expressed in Kupffer cells and exudate macrophages in the liver, especially in granulomas. Larger numbers of T cells and natural killer T (NKT) cells underwent apoptosis in the granulomas of AIM(-/-) mice, suggesting that AIM prevents apoptosis of NKT cells and T cells in C. parvum-induced inflammation. Recombinant AIM (rAIM) protein significantly inhibited apoptosis of NKT cells and T cells obtained from C. parvum-stimulated livers in vitro. These results indicate that AIM functions to induce resistance to apoptosis within NKT cells and T cells, and supports the host defense in granulomatous inflammation.
Figures





References
-
- Oyama H, Yamada T, Inoue Y: Effect of post-irradiation temperature on viability of rat thymocytes. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med 1974, 26:535-546 - PubMed
-
- Ohyama H, Yamada T, Ohkawa A, Watanabe I: Radiation-induced formation of apoptotic bodies in rat thymus. Radiat Res 1985, 101:123-130 - PubMed
-
- Bodey B, Bodey B, Jr, Kaiser HE: Apoptosis in the mammalian thymus during normal histogenesis and under various in vitro and in vivo experimental conditions. In Vivo 1998, 12:123-133 - PubMed
-
- Selye H: Thymus and adrenals in the response of the organism to injuries and intoxication. Br J Exp Pathol 1936, 17:234-248
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

