Dystroglycan expression is frequently reduced in human breast and colon cancers and is associated with tumor progression
- PMID: 12598319
- PMCID: PMC1868099
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63881-3
Dystroglycan expression is frequently reduced in human breast and colon cancers and is associated with tumor progression
Abstract
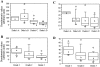
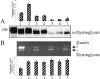
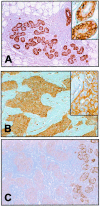
Dystroglycan (DG) is an adhesion molecule responsible for crucial interactions between extracellular matrix and cytoplasmic compartment. It is formed by two subunits, alpha-DG (extracellular) and beta-DG (transmembrane), that bind to laminin in the matrix and dystrophin in the cytoskeleton, respectively. In this study we evaluated by Western blot analysis the expression of DG in a series of human cancer cell lines of various histogenetic origin and in a series of human primary colon and breast cancers. Decreased expression of DG was observed in most of the cell lines and in both types of tumors and correlated with higher tumor grade and stage. Analysis of the mRNA levels suggested that expression of DG protein is likely regulated at a posttranscriptional level. Evaluation of alpha-DG expression by immunostaining in a series of archival cases of primary breast carcinomas confirmed that alpha-DG expression is lost in a significant fraction of tumors (66%). Loss of DG staining correlated with higher tumor stage (P = 0.022), positivity for p53 (P = 0.033), and high proliferation index (P = 0.045). A significant correlation was also observed between loss of alpha-DG and overall survival (P = 0.013 by log-rank test) in an univariate analysis. These data indicate that DG expression is frequently lost in human malignancies and suggest that this glycoprotein might play an important role in human tumor development and progression.
Figures



References
-
- Durbeej M, Henry MD, Ferletta M, Campbell KP, Ekblom P: Distribution of dystroglycan in normal adult mouse tissues. J Histochem Cytochem 1998, 46:449-457 - PubMed
-
- Winder SJ: The complexities of dystroglycan. Trends Biochem Sci 2001, 26:118-124 - PubMed
-
- Holt KH, Crosbie RH, Venzke DP, Campbell KP: Biosynthesis of dystroglycan: processing of a precursor peptide. FEBS Lett 2000, 468:79-83 - PubMed
-
- Ibraghimov-Beskrovnaya O, Ervasti JM, Leveille CJ, Slaughter CA, Sernett SW, Campbell KP: Primary structure of dystrophin-associated glycoproteins linking dystrophin to the extracellular matrix. Nature 1992, 355:696-702 - PubMed
-
- Ibraghimov-Beskrovnaya O, Mialtovich A, Ozcelik T, Yang B, Koepnick K, Francke U, Campbell KP: Human dystroglycan: skeletal muscle cDNA, genomic structure, origin of tissue specific isoforms and chromosomal localization. Hum Mol Genet 1993, 2:1651-1657 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

