Nucleic acid recognition by OB-fold proteins
- PMID: 12598368
- PMCID: PMC1564333
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.32.110601.142506
Nucleic acid recognition by OB-fold proteins
Abstract
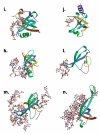
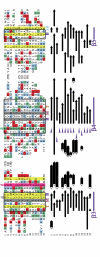
The OB-fold domain is a compact structural motif frequently used for nucleic acid recognition. Structural comparison of all OB-fold/nucleic acid complexes solved to date confirms the low degree of sequence similarity among members of this family while highlighting several structural sequence determinants common to most of these OB-folds. Loops connecting the secondary structural elements in the OB-fold core are extremely variable in length and in functional detail. However, certain features of ligand binding are conserved among OB-fold complexes, including the location of the binding surface, the polarity of the nucleic acid with respect to the OB-fold, and particular nucleic acid-protein interactions commonly used for recognition of single-stranded and unusually structured nucleic acids. Intriguingly, the observation of shared nucleic acid polarity may shed light on the longstanding question concerning OB-fold origins, indicating that it is unlikely that members of this family arose via convergent evolution.
Figures
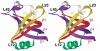
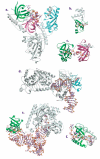
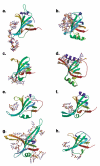
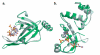

Similar articles
-
OB-fold: growing bigger with functional consistency.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2003 Jun;4(3):195-206. doi: 10.2174/1389203033487207. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2003. PMID: 12769718 Review.
-
BOF: a novel family of bacterial OB-fold proteins.FEBS Lett. 2004 Jun 4;567(2-3):297-301. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.04.086. FEBS Lett. 2004. PMID: 15178340
-
Functional characteristics of small proteins (70 amino acid residues) forming protein-nucleic acid complexes.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2009 Jun;26(6):663-77. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2009.10507280. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2009. PMID: 19385696
-
OB-fold domains: a snapshot of the evolution of sequence, structure and function.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2002 Dec;12(6):794-801. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(02)00392-5. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2002. PMID: 12504685 Review.
-
From RPA to BRCA2: lessons from single-stranded DNA binding by the OB-fold.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2004 Feb;14(1):36-42. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2004.01.001. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2004. PMID: 15102447 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural Basis for Toxin Inhibition in the VapXD Toxin-Antitoxin System.Structure. 2021 Feb 4;29(2):139-150.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2020.10.002. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Structure. 2021. PMID: 33096014 Free PMC article.
-
The structure of KPN03535 (gi|152972051), a novel putative lipoprotein from Klebsiella pneumoniae, reveals an OB-fold.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2010 Oct 1;66(Pt 10):1254-60. doi: 10.1107/S1744309109018168. Epub 2009 Oct 27. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2010. PMID: 20944219 Free PMC article.
-
A dynamic model for replication protein A (RPA) function in DNA processing pathways.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(15):4126-37. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl550. Epub 2006 Aug 25. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16935876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The zinc-fingers of KREPA3 are essential for the complete editing of mitochondrial mRNAs in Trypanosoma brucei.PLoS One. 2010 Jan 27;5(1):e8913. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008913. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20111718 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosines involved in the activity of φ29 single-stranded DNA binding protein.PLoS One. 2019 May 20;14(5):e0217248. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217248. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31107918 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allison TJ, Wood TC, Briercheck DM, Rastinejad F, Richardson JP, Rule GS. Crystal structure of the RNA-binding domain from transcription termination factor rho. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1998;5:352–56. - PubMed
-
- Anderson EM, Halsey WH, Wuttke DS. Site-directed mutagenesis reveals the thermodynamic requirements for single-stranded DNA recognition by the telomere-binding protein Cdc13. Biochemistry. 2002;42 In press. - PubMed
-
- Antson AA. Single stranded RNA binding proteins. Curr. Opin.Struct. Biol. 2000;10:87–94. - PubMed
-
- Ban N, Nissen P, Hansen J, Moore PB, Steitz TA. The completeatomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 Å resolution. Science. 2000;289:905–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
