The CB1 receptor antagonist SR141716A selectively increases monoaminergic neurotransmission in the medial prefrontal cortex: implications for therapeutic actions
- PMID: 12598408
- PMCID: PMC1573706
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705100
The CB1 receptor antagonist SR141716A selectively increases monoaminergic neurotransmission in the medial prefrontal cortex: implications for therapeutic actions
Abstract
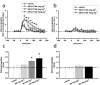
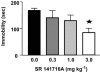
1. In order to explore potential therapeutic implications of cannabinoid antagonists, the effects of the prototypical cannabinoid antagonist SR141716A on monoamine efflux from the medial prefrontal cortex and the nucleus accumbens of the rat were investigated by in vivo microdialysis. 2. SR141716A moderately increased serotonin efflux and concentrations of its metabolite 5-HIAA, both in the medial prefrontal cortex and the nucleus accumbens, and increased norepinephrine, dopamine and their metabolites in the medial prefrontal cortex. In contrast, it had no effect on norepinephrine, dopamine and their metabolites in the nucleus accumbens. 3. At the same doses, SR141716A increased acetylcholine efflux in the medial prefrontal cortex, in agreement with previous studies; contrary to the effects in cortex, SR141716A had no effect on acetylcholine efflux in the nucleus accumbens. 4. The efficacy of SR141716A in the psychostimulant-induced hyperlocomotion and the forced swimming paradigms was also explored in mice. SR141716A attenuated phenylcyclidine- and d-amphetamine-induced hyperlocomotion, without affecting locomotor activity when administered alone, and decreased immobility in the forced swimming test. 5. These results suggest that the cortical selectivity in the release of catecholamines, dopamine in particular, induced by the cannabinoid antagonist SR141716A, its procholinergic properties, together with its mild stimulatory effects on serotonin and norepinephrine efflux make similar compounds unique candidates for the treatment of psychosis, affective and cognitive disorders.
Figures
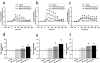



References
-
- ACQUAS E., PISANU A., MARROCU P., DI CHIARA G. Cannabinoid CB(1) receptor agonists increase rat cortical and hippocampal acetylcholine release in vivo. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000;401:179–185. - PubMed
-
- ALONSO R., VOUTSINOS B., FOURNIER M., LABIE C., STEINBERG R., SOUILHAC J., LE FUR G., SOUBRIE P. Blockade of cannabinoid receptors by SR141716 selectively increases Fos expression in rat mesocorticolimbic areas via reduced dopamine D2 function. Neuroscience. 1999;91:607–620. - PubMed
-
- ARBORELIUS L., NOMIKOS G.G., HACKSELL U., SVENSSON T.H. (R)-8-OH-DPAT preferentially increases dopamine release in rat medial prefrontal cortex. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1993;148:465–466. - PubMed
-
- AUCLAIR N., OTANI S., SOUBRIE P., CREPEL F. Cannabinoids modulate synaptic strength and plasticity at glutamatergic synapses of rat prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2000;83:3287–3293. - PubMed
-
- BAXTER L.R., JR, SCHWARTZ J.M., PHELPS M.E., MAZZIOTTA J.C., GUZE B.H., SELIN C.E., GERNER R.H., SUMIDA R.M. Reduction of prefrontal cortex glucose metabolism common to three types of depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry. 1989;46:243–250. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

