Selective blockade of endothelial Ca2+-activated small- and intermediate-conductance K+-channels suppresses EDHF-mediated vasodilation
- PMID: 12598413
- PMCID: PMC1573692
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705075
Selective blockade of endothelial Ca2+-activated small- and intermediate-conductance K+-channels suppresses EDHF-mediated vasodilation
Abstract
1. Activation of Ca(2+)-activated K(+)-channels (K(Ca)) has been suggested to play a key role in endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor (EDHF)-mediated vasodilation. However, due to the low selectivity of commonly used K(Ca)-channel blockers it is still elusive which endothelial K(Ca)-subtypes mediate hyperpolarization and thus initiate EDHF-mediated vasodilation. 2. Using the non-cytochrome P450 blocking clotrimazole-derivatives, 1-[(2-chlorophenyl) diphenylmethyl]-1H-pyrazole (TRAM-34) and 2-(2-chlorophenyl)-2,2-diphenylacetonitrile (TRAM-39) as highly selective IK1-inhibitors, we investigated the role of the intermediate-conductance K(Ca) (rIK1) in endothelial hyperpolarization and EDHF-mediated vasodilation. 3. Expression and function of rIK1 and small-conductance K(Ca) (rSK3) were demonstrated in situ in single endothelial cells of rat carotid arteries (CA). rIK1-currents were blocked by TRAM-34 or TRAM-39, while rSK3 was blocked by apamin. In current-clamp experiments, endothelial hyperpolarization in response to acetylcholine was abolished by the combination of apamin and TRAM-34. 4. In phenylephrine-preconstricted CA, acetylcholine-induced NO and prostacyclin-independent vasodilation was almost completely blocked by ChTX, CLT, TRAM-34, or TRAM-39 in combination with the SK3-blocker apamin. Apamin, TRAM-34, and CLT alone or sulphaphenzole, a blocker of the cytochrome P450 isoform 2C9, were ineffective in blocking the EDHF-response. 5. In experiments without blocking NO and prostacyclin synthesis, the combined blockade of SK3 and IK1 reduced endothelium-dependent vasodilation. 6. In conclusion, the use of selective IK1-inhibitors together with the SK3-blocker apamin revealed that activation of both K(Ca), rIK1 and rSK3 is crucial in mediating endothelial hyperpolarization and generation of the EDHF-signal while the cytochrome P450 pathway seems to play a minor or no role in rat CA.
Figures
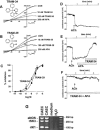



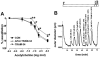
Comment in
-
EDHF and endothelial potassiun channels: IKCa and SKCa.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Sep;140(1):225; author reply 226. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705425. Epub 2003 Aug 4. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12967953 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- ADAMS D.J., BARAKEH J., LASKEY R., VAN BREEMEN C. Ion channels and regulation of intracellular calcium in vascular endothelial cells. FASEB J. 1989;3:2389–2400. - PubMed
-
- ANDERSSON D.A., ZYGMUNT P.M., MOVAHED P., ANDERSSON T.L., HOGESTATT E.D. Effects of inhibitors of small- and intermediate-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels, inwardly-rectifying potassium channels and Na(+)/K(+) ATPase on EDHF relaxations in the rat hepatic artery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000;129:1490–1496. - PMC - PubMed
-
- BOLZ S.S., FISSLTHALER B., PIEPERHOFF S., DE WIT C., FLEMING I., BUSSE R., POHL U. Antisense oligonucleotides against cytochrome P450 2C8 attenuate EDHF-mediated Ca(2+) changes and dilation in isolated resistance arteries. FASEB J. 2000;14:255–260. - PubMed
-
- CHAYTOR A,T., MARTIN P.E., EDWARDS D.H., GRIFFITH T.M. Gap junctional communication underpins EDHF-type relaxations evoked by ACh in the rat hepatic artery. Am. J. Physiol. Heart. Circ. Physiol. 2001;280:H2441–H2450. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

