G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 (GRK6) selectively regulates endogenous secretin receptor responsiveness in NG108-15 cells
- PMID: 12598420
- PMCID: PMC1573707
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705101
G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 (GRK6) selectively regulates endogenous secretin receptor responsiveness in NG108-15 cells
Abstract
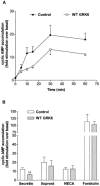
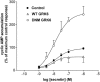
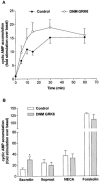
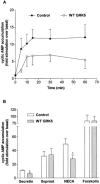
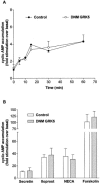
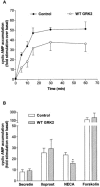
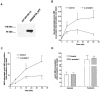
1. To determine the role of G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs) in the regulation of endogenous secretin receptor responsiveness, we have transiently overexpressed both wild-type (WT) and dominant negative mutant (DNM) GRKs in NG108-15 mouse neuroblastoma x rat glioma hybrid cells and investigated the effects of this on agonist-stimulated adenylyl cyclase activity. 2. Overexpression of WT GRK6 selectively inhibited secretin-stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation (fold stimulation of cyclic AMP above basal following 15 min incubation with 100 nM secretin was 12.1+/-2.0 and 6.2+/- 0.8 in control and WT GRK overexpressing cells, respectively) without affecting cyclic AMP responses mediated by the adenosine A(2) receptor agonist 5'-(N-ethylcarboxamido) adenosine (NECA) or the prostanoid-IP receptor agonist iloprost, or the direct activator of adenylyl cyclase, forskolin. On the other hand DNM GRK6 (Lys(215)Arg) overexpression produced the opposite effect--a selective increase in the secretin-stimulated cyclic AMP response was observed in cells overexpressing DNM GRK6 compared to plasmid-transfected cells (fold stimulation of cyclic AMP above basal following 15 min incubation with 100 nM secretin was 12.6+/-2.7 and 29.6+/-5.6 for control and DNM GRK6-overexpressing cells, respectively). 3. Overexpression of WT GRK5 likewise inhibited the secretin-stimulated cyclic AMP response, however, this effect was not as selective as with GRK6, since adenosine A(2) receptor responsiveness was also suppressed by GRK5 overexpression. Unlike DNM GRK6, overexpression of DNM GRK5 failed to modulate secretin or A(2) adenosine receptor signalling suggesting that endogenous GRK5 is unlikely to regulate desensitization of these receptors in NG108-15 cells. 4. Overexpression of WT GRK2 did not affect secretin-stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation. Instead, GRK2 overexpression selectively inhibited A(2) adenosine receptor responsiveness, confirming our previous findings. 5. Together these results suggest a selective role of endogenous GRK6 in regulating secretin receptor responsiveness in NG108-15 cells. In addition, these data indicate that GRKs exert a surprising degree of selectivity in the regulation of natively expressed GPCR responses.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Second messenger-dependent protein kinases and protein synthesis regulate endogenous secretin receptor responsiveness.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Apr;135(8):2020-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704655. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11959806 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced expression of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 selectively increases the sensitivity of A2A adenosine receptors to agonist-induced desensitization.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Sep;125(2):347-56. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702081. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9786508 Free PMC article.
-
A dominant negative mutant of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 selectively attenuates adenosine A2 receptor desensitization.Mol Pharmacol. 1997 Jun;51(6):991-8. doi: 10.1124/mol.51.6.991. Mol Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9187265
-
G protein-coupled receptor kinases as regulators of dopamine receptor functions.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Sep;111:1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.05.010. Epub 2016 May 10. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27178731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of regulation and function of G-protein-coupled receptor kinases.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Dec 28;12(48):7753-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i48.7753. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 17203515 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
How regulators of G protein signaling achieve selective regulation.J Mol Biol. 2007 Feb 16;366(2):349-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.11.045. Epub 2006 Nov 15. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17173929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caveolae-dependent internalization and homologous desensitization of VIP/PACAP receptor, VPAC₂, in gastrointestinal smooth muscle.Peptides. 2013 May;43:137-45. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2013.03.008. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Peptides. 2013. PMID: 23499767 Free PMC article.
-
Morphine-induced internalization of the L83I mutant of the rat μ-opioid receptor.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Jan;172(2):593-605. doi: 10.1111/bph.12709. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 24697554 Free PMC article.
-
Second messenger-dependent protein kinases and protein synthesis regulate endogenous secretin receptor responsiveness.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Apr;135(8):2020-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704655. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11959806 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of PKC alpha and G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 in agonist-selective desensitization of mu-opioid receptors in mature brain neurons.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Sep;158(1):157-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00140.x. Epub 2009 Mar 20. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19309357 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AIYAR N., DISA J., DANG K., PRONIN A.N., BENOVIC J.L., NAMBI P. Involvement of G protein-coupled receptor kinase-6 in desensitization of CGRP receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000;403:1–7. - PubMed
-
- BRADFORD M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- CORDEAUX Y., HILL S.J. Mechanisms of cross-talk between G-protein-coupled receptors. Neurosignals. 2002;11:45–57. - PubMed
-
- DAUTZENBERG F.M., HAUGER R.L. G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 3- and protein kinase C- mediated densitization of the PACAP receptor type 1 in human Y-79 retinoblastoma cells. Neuropharmacology. 2001;40:394–407. - PubMed
-
- FERGUSON S.S. Evolving concepts in G protein-coupled receptor endocytosis: the role in receptor desensitization and signaling. Pharmacol. Rev. 2001;53:1–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

