The cyclopentenone prostaglandin 15-deoxy-delta(12,14)- PGJ2 attenuates the development of colon injury caused by dinitrobenzene sulphonic acid in the rat
- PMID: 12598422
- PMCID: PMC1573694
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705077
The cyclopentenone prostaglandin 15-deoxy-delta(12,14)- PGJ2 attenuates the development of colon injury caused by dinitrobenzene sulphonic acid in the rat
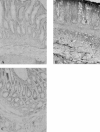
Abstract
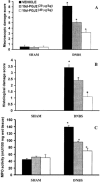
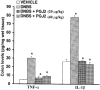
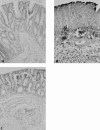
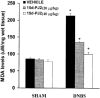
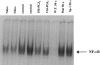
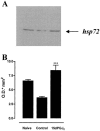
1. Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is characterized by oxidative and nitrosative stress, leukocyte infiltration, and increased expression of the adhesion molecules intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) in the colon. Recent evidence also suggests that the cyclopentenone prostaglandin (PG) 15-deoxy-delta(12,14)-PGJ(2) (15d- PGJ(2)) functions as an early anti-inflammatory signal. 2. The aim of the present paper is to investigate the effects of 15d-PGJ(2) in rats subjected to experimental colitis. 3. Colitis was induced in rats by intra-colonic instillation of dinitrobenzene sulphonic acid (DNBS). 15d-PGJ(2) was administered daily as intraperitoneal injection (20 or 40 microg kg(-1)). On day 4, animals were sacrificed and tissues were taken for histological and biochemical analysis. 4. 15d-PGJ(2) significantly reduced the degree of haemorrhagic diarrhoea and weight loss caused by administration of DNBS. 15d-PGJ(2) also caused a substantial reduction of (i) the degree of colonic injury, (ii) the rise in myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity (mucosa), (iii) the increase in the tissue levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) and (iv) of the pro-inflammatory cytokines tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta). 5. Furthermore, 15d-PGJ(2) reduced the increase in immunohistochemical staining for (i) inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), (ii) nitrotyrosine and (iii) poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), as well as (iv) the increased expression of ICAM-1 caused by DNBS in the colon. 6. Electrophoresis mobility shift assay (EMSA) of inflamed colon revealed that 15d- PGJ(2) also caused a substantial reduction of the activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB). Furthermore, 15d-PGJ(2) stimulates the activation of heat shock protein 72 (hsp72) in the inflamed colon, as assessed by Western blot analysis. 7. In conclusion, 15d-PGJ(2) reduces the development of experimental colitis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Teupolioside, a phenylpropanoid glycosides of Ajuga reptans, biotechnologically produced by IRBN22 plant cell line, exerts beneficial effects on a rodent model of colitis.Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Mar 1;77(5):845-57. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.11.010. Epub 2008 Nov 25. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19070602
-
Thalidomide treatment reduces colon injury induced by experimental colitis.Shock. 2005 Jun;23(6):556-64. Shock. 2005. PMID: 15897810
-
Calpain inhibitor I reduces colon injury caused by dinitrobenzene sulphonic acid in the rat.Gut. 2001 Apr;48(4):478-88. doi: 10.1136/gut.48.4.478. Gut. 2001. PMID: 11247891 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclopentenone prostaglandins: new insights on biological activities and cellular targets.Med Res Rev. 2001 May;21(3):185-210. doi: 10.1002/med.1006. Med Res Rev. 2001. PMID: 11301410 Review.
-
The effects of Delta(12)-PGJ(2) on malignant cells.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2000 Jun;62(1):75-90. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(00)00076-9. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2000. PMID: 10936416 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
NF-kappaB activation precedes increases in mRNA encoding neurokinin-1 receptor, proinflammatory cytokines, and adhesion molecules in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in rats.Dig Dis Sci. 2005 Dec;50(12):2366-78. doi: 10.1007/s10620-005-3066-y. Dig Dis Sci. 2005. PMID: 16416193
-
PPARγ and the Innate Immune System Mediate the Resolution of Inflammation.PPAR Res. 2015;2015:549691. doi: 10.1155/2015/549691. Epub 2015 Dec 2. PPAR Res. 2015. PMID: 26713087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The cyclopentenone prostaglandin 15-deoxydelta(12,14)-prostaglandin J2 attenuates the development of zymosan-induced shock.Intensive Care Med. 2005 May;31(5):693-700. doi: 10.1007/s00134-005-2596-2. Epub 2005 Mar 15. Intensive Care Med. 2005. PMID: 15868139
-
Interventions of natural and synthetic agents in inflammatory bowel disease, modulation of nitric oxide pathways.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Jun 28;26(24):3365-3400. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i24.3365. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32655263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual role of melatonin as an anti-colitis and anti-extra intestinal alterations against acetic acid-induced colitis model in rats.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 15;12(1):6344. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-10400-y. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35428860 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AIKO S., GRISHAM M.B. Spontaneous intestinal inflammation and nitric oxide metabolism in HLA-B27 transgenic rats. Gastroenterology. 1995;109:142–150. - PubMed
-
- AJUEBOR M.N., SINGH A., WALLACE J.L. Cyclooxygenase-2-derived prostaglandin D(2) is an early anti-inflammatory signal in experimental colitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2000;279:G238–G244. - PubMed
-
- BAUERLE P.A., HENKEL T. Function and activation of NF-κB in the immune system. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 1994;2:141–179. - PubMed
-
- BECKMAN J.S. Oxidative damage and tyrosine nitration from peroxynitrite. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1996;9:836–844. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

