Paravertebral primitive neuroectodermal tumour presenting with Horner's syndrome
- PMID: 12598461
- PMCID: PMC1771548
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.87.3.366-a
Paravertebral primitive neuroectodermal tumour presenting with Horner's syndrome
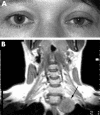
Figures

Similar articles
-
Primitive neuroectodermal tumour presenting with subarachnoid haemorrhage.Br J Neurosurg. 1994;8(2):209-14. doi: 10.3109/02688699409027970. Br J Neurosurg. 1994. PMID: 7917095 Review.
-
[Horner's syndrome and brachial radiculopathy related to vertebral metastases].Rev Neurol. 1999 Oct 1-15;29(7):614-6. Rev Neurol. 1999. PMID: 10599108 Spanish.
-
Pancoast tumour presenting as paraplegia with Horner's syndrome.J Assoc Physicians India. 2010 Apr;58:232. J Assoc Physicians India. 2010. PMID: 21046878 No abstract available.
-
Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor in a Child with Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection: A Rare Association.J Trop Pediatr. 2020 Feb 1;66(1):106-109. doi: 10.1093/tropej/fmz034. J Trop Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 31257424
-
[An adult case of congenital Horner's syndrome with heterochromia iridis--with special reference to alteration of Horner's sign associated with development].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1989 Oct;29(10):1278-82. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1989. PMID: 2691167 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Schwannoma of cervical sympathetic chain: assessment and management.Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2005 Jun;25(3):191-4. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2005. PMID: 16450776 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kawasaki A. Physiology, assessment, and disorders of the pupil. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 1999;10:394–400. - PubMed
-
- Amonoo-Kuofi HS. Horner’s syndrome revisited: with an update of the central pathway. Clin Anat 1999;12:345–61. - PubMed
-
- Wilhelm H. Neuro-ophthalmology of pupillary function—practical guidelines. J Neurol 1998;245:573–83. - PubMed
-
- Nielsen PJ. Upside down ptosis in patients with Horner’s syndrome. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1983;61:952–7. - PubMed
-
- Jones JE, McGill T. Peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumors of the head and neck. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1995;121:1392–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
