Modulation of the kv3.1b potassium channel isoform adjusts the fidelity of the firing pattern of auditory neurons
- PMID: 12598601
- PMCID: PMC6742259
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-04-01133.2003
Modulation of the kv3.1b potassium channel isoform adjusts the fidelity of the firing pattern of auditory neurons
Abstract
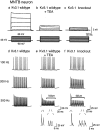
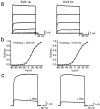
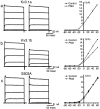
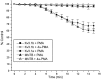
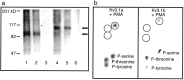
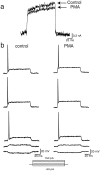
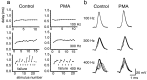
Neurons of the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body, which transmit auditory information that is used to compute the location of sounds in space, are capable of firing at high frequencies with great temporal precision. We found that elimination of the Kv3.1 gene in mice results in the loss of a high-threshold component of potassium current and failure of the neurons to follow high-frequency stimulation. A partial decrease in Kv3.1 current can be produced in wild-type neurons of the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body by activation of protein kinase C. Paradoxically, activation of protein kinase C increases temporal fidelity and the number of action potentials that are evoked by intermediate frequencies of stimulation. Computer simulations confirm that a partial decrease in Kv3.1 current is sufficient to increase the accuracy of response at intermediate frequencies while impairing responses at high frequencies. We further establish that, of the two isoforms of the Kv3.1 potassium channel that are expressed in these neurons, Kv3.1a and Kv3.1b, the decrease in Kv3.1 current is mediated by selective phosphorylation of the Kv3.1b isoform. Using site-directed mutagenesis, we identify a specific C-terminal phosphorylation site responsible for the observed difference in response of the two isoforms to protein kinase C activation. Our results suggest that modulation of Kv3.1 by phosphorylation allows auditory neurons to tune their responses to different patterns of sensory stimulation.
Figures


References
-
- Critz SD, Wible BA, Lopez HS, Brown AM. Stable expression and regulation of a rat brain K channel. J Neurochem. 1993;60:1175–1178. - PubMed
-
- Grigg JJ, Brew HM, Tempel BL. Differential expression of voltage-gated potassium channel genes in auditory nuclei of the mouse brainstem. Hear Res. 2000;140:77–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
