Neuronal hyperpolarization-activated pacemaker channels drive neuropathic pain
- PMID: 12598605
- PMCID: PMC6742242
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-04-01169.2003
Neuronal hyperpolarization-activated pacemaker channels drive neuropathic pain
Abstract
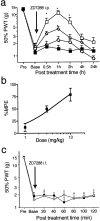
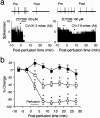
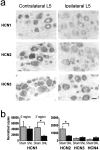
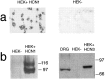
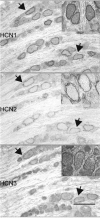
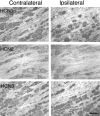
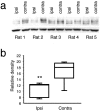
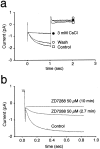
Neuropathic pain is a common and often incapacitating clinical problem for which little useful therapy is presently available. Painful peripheral neuropathies can have many etiologies, among which are trauma, viral infections, exposure to radiation or chemotherapy, and metabolic or autoimmune diseases. Sufferers generally experience both pain at rest and exaggerated, painful sensitivity to light touch. Spontaneous firing of injured nerves is believed to play a critical role in the induction and maintenance of neuropathic pain syndromes. Using a well characterized nerve ligation model in the rat, we demonstrate that hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic nucleotide-modulated (HCN) "pacemaker" channels play a previously unrecognized role in both touch-related pain and spontaneous neuronal discharge originating in the damaged dorsal root ganglion. HCN channels, particularly HCN1, are abundantly expressed in rat primary afferent somata. Nerve injury markedly increases pacemaker currents in large-diameter dorsal root ganglion neurons and results in pacemaker-driven spontaneous action potentials in the ligated nerve. Pharmacological blockade of HCN activity using the specific inhibitor ZD7288 reverses abnormal hypersensitivity to light touch and decreases the firing frequency of ectopic discharges originating in Abeta and Adelta fibers by 90 and 40%, respectively, without conduction blockade. These findings suggest novel insights into the molecular basis of pain and the possibility of new, specific, effective pharmacological therapies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Involvement of hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channels in dorsal root ganglion in neuropathic pain.Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2008 Oct 25;60(5):579-80. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2008. PMID: 18958363
-
Hyperpolarization-activated, cation-nonselective, cyclic nucleotide-modulated channel blockade alleviates mechanical allodynia and suppresses ectopic discharge in spinal nerve ligated rats.J Pain. 2005 Jul;6(7):417-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2005.02.002. J Pain. 2005. PMID: 15993819
-
Membrane potential oscillations are not essential for spontaneous firing generation in L4 Aβ-afferent neurons after L5 spinal nerve axotomy and are not mediated by HCN channels.Exp Physiol. 2018 Aug;103(8):1145-1156. doi: 10.1113/EP087013. Epub 2018 Jun 26. Exp Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29860719
-
Hyperpolarization-activated and cyclic nucleotide-gated channel proteins as emerging new targets in neuropathic pain.Rev Neurosci. 2019 Jul 26;30(6):639-649. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2018-0094. Rev Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30768426 Review.
-
Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels and pain.Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15(15):1767-72. doi: 10.2174/138161209788186281. Curr Pharm Des. 2009. PMID: 19442189 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of small fiber pathology in a mouse model of Fabry disease.Elife. 2018 Oct 17;7:e39300. doi: 10.7554/eLife.39300. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30328411 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Prostaglandin E1 as a Pain Mediator through Facilitation of Hyperpolarization-Activated Cyclic Nucleotide-Gated Channel 2 via the EP2 Receptor in Trigeminal Ganglion Neurons of Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 16;22(24):13534. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413534. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948328 Free PMC article.
-
Funny currents are becoming serious players in nociceptor's sensitization.J Physiol. 2008 Dec 15;586(24):5841-2. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.165852. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 19074817 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Upregulation of Ih expressed in IB4-negative Aδ nociceptive DRG neurons contributes to mechanical hypersensitivity associated with cervical radiculopathic pain.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 18;5:16713. doi: 10.1038/srep16713. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26577374 Free PMC article.
-
HCN Channels Modulators: The Need for Selectivity.Curr Top Med Chem. 2016;16(16):1764-91. doi: 10.2174/1568026616999160315130832. Curr Top Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26975509 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdi S, Lee DH, Park SK, Chung JM. Lack of pre-emptive analgesic effects of local anaesthetics on neuropathic pain. Br J Anaesth. 2000;85:620–623. - PubMed
-
- Abdulla FA, Smith PA. Axotomy- and autotomy-induced changes in Ca2+ and K+ channel currents of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Neurophysiol. 2001;85:644–658. - PubMed
-
- Beaumont V, Zucker RS. Enhancement of synaptic transmission by cyclic AMP modulation of presynaptic Ih channels. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:133–141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
