GTPase regulators and photoresponses in cones of the eastern chipmunk
- PMID: 12598617
- PMCID: PMC6742256
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-04-01287.2003
GTPase regulators and photoresponses in cones of the eastern chipmunk
Abstract
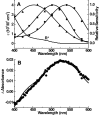
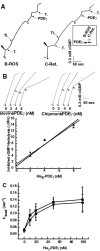
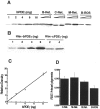
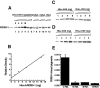
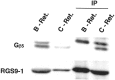
Vertebrate cone and rod photoreceptor cells use similar mechanisms to transduce light signals into electrical signals, but their responses to light differ in sensitivity and kinetics. To assess the role of G-protein GTP hydrolysis kinetics in mammalian cone photoresponses, we have characterized photoresponses and GTPase regulatory components of cones and rods from the cone-dominant retina of the eastern chipmunk. Sensitivity, based on the stimulus strength required for a half-maximum response, of the M-cone population was 38-fold lower than that of the rods. The relatively lower cone sensitivity could be attributed in part to lower amplification in the rising phase and in part to faster recovery kinetics. At a molecular level, cloning of chipmunk cDNA and expression of recombinant proteins provided standards for quantitative immunoblot analysis of proteins involved in GTPase acceleration. The ratio of the cGMP-phosphodiesterase inhibitory subunit gamma to cone pigment, 1:68, was similar to the levels observed for ratios to rhodopsin in bovine retina, 1:76, or mouse retina, 1:65. In contrast, the ratio to pigment of the GTPase-accelerating protein RGS9-1 was 1:62, more than 10 times higher than ratios observed in rod-dominant retinas. Immunoprecipitation experiments revealed that, in contrast to rods, RGS9-1 in chipmunk retina is associated with both the short and long isoforms of its partner subunit G(beta5). The much higher levels of the GTPase-accelerating protein complex in cones, compared with rods, suggest a role for GTPase acceleration in obtaining rapid photoresponse kinetics.
Figures



References
-
- Angleson JK, Wensel TG. Enhancement of rod outer segment GTPase accelerating protein activity by the inhibitory subunit of cGMP phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:16290–16296. - PubMed
-
- Arshavsky VY, Lamb TD, Pugh EN., Jr G proteins and phototransduction. Annu Rev Physiol. 2002;64:153–187. - PubMed
-
- Babu KR, Dukkipati A, Birge RR, Knox BE. Regulation of phototransduction in short-wavelength cone visual pigments via the retinylidene Schiff base counterion. Biochemistry. 2001;40:13760–13766. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
