Oestrogen receptor specificity in oestradiol-mediated effects on B lymphopoiesis and immunoglobulin production in male mice
- PMID: 12603601
- PMCID: PMC1782901
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2003.01599.x
Oestrogen receptor specificity in oestradiol-mediated effects on B lymphopoiesis and immunoglobulin production in male mice
Abstract
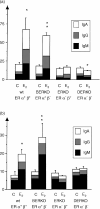
Oestrogen treatment down-regulates B lymphopoiesis in the bone marrow of mice. Meanwhile it up-regulates immunoglobulin production. To understand better the oestrogen action on bone marrow male mice lacking oestrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha; ERKO mice), lacking ERbeta (BERKO mice), lacking both receptors (DERKO mice) or wild-type (wt) littermates were castrated and treated for 2.5 weeks with 30 microg/kg 17beta-oestradiol (E2) or vehicle oil as controls. The B lymphopoiesis in the bone marrow was examined by flow cytometry and mature B-cell function was studied using an ELISPOT assay enumerating the B cells in bone marrow and spleen that were actively producing immunoglobulins. In wt mice the frequency of B-lymphopoietic (B220+) cells in the bone marrow decreased from 15% to 5% upon E2 treatment. In ERKO and BERKO mice significant reduction was seen but not of the same magnitude. In DERKO mice no reduction of B lymphopoiesis was seen. In addition, our results show that E2 mediated reduction of different steps in B lymphopoiesis require only ERalpha or both receptors. In wt and BERKO mice E2 treatment resulted in significantly increased levels of B cells actively producing immunoglobulin, while in ERKO and DERKO mice no such change was seen. Similar results were found in both bone marrow and spleen. In conclusion our results clearly show that both ERalpha and ERbeta are required for complete down-regulation of B lymphopoiesis while only ERalpha is needed to up-regulate immunoglobulin production in both bone marrow and spleen.
Figures


References
-
- Medina KL, Strasser A, Kincade PW. Estrogen influences the differentiation, proliferation, and survival of early B-lineage precursors. Blood. 2000;95:2059–67. - PubMed
-
- Rijhsinghani AG, Thompson K, Bhatia SK, Waldschmidt TJ. Estrogen blocks early T cell development in the thymus. Am J Reprod Immunol. 1996;36:269–77. - PubMed
-
- Josefsson E, Tarkowski A, Carlsten H. Anti-inflammatory properties of estrogen. I. In vivo suppression of leukocyte production in bone marrow and redistribution of peripheral blood neutrophils. Cell Immunol. 1992;142:67–78. - PubMed
-
- Carlsten H, Verdrengh M, Taube M. Additive effects of suboptimal doses of estrogen and cortisone on the suppression of T lymphocyte dependent inflammatory responses in mice. Inflamm Res. 1996;45:26–30. - PubMed
-
- Hanna N, Schneider M. Enhancement of tumor metastasis and suppression of natural killer cell activity by beta-estradiol treatment. J Immunol. 1983;130:974–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

