Elimination of epidemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from a university hospital and district institutions, Finland
- PMID: 12603986
- PMCID: PMC2901945
- DOI: 10.3201/eid0902.020233
Elimination of epidemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from a university hospital and district institutions, Finland
Abstract
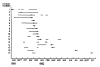
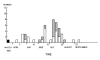
From August 1991 to October 1992, two successive outbreaks of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) occurred at a hospital in Finland. During and after these outbreaks, MRSA was diagnosed in 202 persons in our medical district; >100 cases involved epidemic MRSA. When control policies failed to stop the epidemic, more aggressive measures were taken, including continuous staff education, contact isolation for MRSA-positive patients, systematic screening for persons exposed to MRSA, cohort nursing of MRSA-positive and MRSA-exposed patients in epidemic situations, and perception of the 30 medical institutions in that district as one epidemiologic entity brought under surveillance and control of the infection control team of Turku University Hospital. Two major epidemic strains, as well as eight additional strains, were eliminated; we were also able to prevent nosocomial spread of other MRSA strains. Our data show that controlling MRSA is possible if strict measures are taken before the organism becomes endemic. Similar control policies may be successful for dealing with new strains of multiresistant bacteria, such as vancomycin-resistant strains of S. aureus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Control of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a hospital and an intensive care unit.Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1995 Jul;16(7):405-11. doi: 10.1086/647138. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1995. PMID: 7673646
-
Effectiveness of preemptive barrier precautions in controlling nosocomial colonization and infection by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a burn unit.Am J Infect Control. 2006 Oct;34(8):476-83. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2006.01.011. Am J Infect Control. 2006. PMID: 17015152
-
Control of epidemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a Dutch university hospital.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Jan;10(1):6-11. doi: 10.1007/BF01967090. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991. PMID: 2009885
-
Nosocomial staphylococcal outbreaks.Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1994;93:47-54. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1994. PMID: 8047857 Review.
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Past, present, and future.Nurs Clin North Am. 1993 Sep;28(3):625-37. Nurs Clin North Am. 1993. PMID: 8367329 Review.
Cited by
-
Concurrent analysis of nose and groin swab specimens by the IDI-MRSA PCR assay is comparable to analysis by individual-specimen PCR and routine culture assays for detection of colonization by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.J Clin Microbiol. 2006 Aug;44(8):2904-8. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02211-05. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16891510 Free PMC article.
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Europe, 1999-2002.Emerg Infect Dis. 2004 Sep;10(9):1627-34. doi: 10.3201/eid1009.040069. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004. PMID: 15498166 Free PMC article.
-
Prophage Typing of Staphylococcus aureus Strains Isolated from Broiler Poultry.Arch Razi Inst. 2021 Sep 1;76(3):499-506. doi: 10.22092/ari.2020.343199.1498. eCollection 2021 Summer. Arch Razi Inst. 2021. PMID: 34824743 Free PMC article.
-
Clonality of epidemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains in Finland as defined by several molecular methods.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2008 Jul;27(7):545-55. doi: 10.1007/s10096-008-0470-1. Epub 2008 Feb 15. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 18274796
-
Changing epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a low endemicity area-new challenges for MRSA control.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020 Dec;39(12):2299-2307. doi: 10.1007/s10096-020-03824-9. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 31989375 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Diekema DJ, Pfaller MA, Schmitz FJ, Smayevsky J, Bell J, Jones RN, et al. Survey of infections due to Staphylococcus species: frequency of occurrence and antimicrobial susceptibility of isolates collected in the United States, Canada, Latin America, Europe, and the Western Pacific Region for the SENTRY antimicrobial surveillance program, 1997–1999. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32(Suppl 2):114–32. 10.1086/320184 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
