Alteration of Escherichia coli topoisomerase IV to novobiocin resistance
- PMID: 12604525
- PMCID: PMC149342
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.3.941-947.2003
Alteration of Escherichia coli topoisomerase IV to novobiocin resistance
Abstract
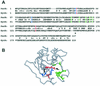
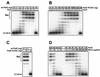
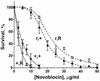
DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV (topo IV) are the two essential type II topoisomerases of Escherichia coli. Gyrase is responsible for maintaining negative supercoiling of the bacterial chromosome, whereas topo IV's primary role is in disentangling daughter chromosomes following DNA replication. Coumarins, such as novobiocin, are wide-spectrum antimicrobial agents that primarily interfere with DNA gyrase. In this work we designed an alteration in the ParE subunit of topo IV at a site homologous to that which confers coumarin resistance in gyrase. This parE mutation renders the encoded topo IV approximately 40-fold resistant to inhibition by novobiocin in vitro and imparts a similar resistance to inhibition of topo IV-mediated relaxation of supercoiled DNA in vivo. We conclude that topo IV is a secondary target of novobiocin and that it is very likely to be inhibited by the same mechanism as DNA gyrase.
Figures
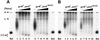
Similar articles
-
Contribution of the ATP binding site of ParE to susceptibility to novobiocin and quinolones in Streptococcus pneumoniae.J Bacteriol. 2005 Feb;187(4):1536-40. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.4.1536-1540.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 15687222 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of Escherichia coli topoisomerase IV ParE subunit (24 and 43 kilodaltons): a single residue dictates differences in novobiocin potency against topoisomerase IV and DNA gyrase.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 May;48(5):1856-64. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.5.1856-1864.2004. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004. PMID: 15105144 Free PMC article.
-
Active-site residues of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase required in coupling ATP hydrolysis to DNA supercoiling and amino acid substitutions leading to novobiocin resistance.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003 Mar;47(3):1037-46. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.3.1037-1046.2003. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. PMID: 12604539 Free PMC article.
-
What makes a type IIA topoisomerase a gyrase or a Topo IV?Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jun 21;49(11):6027-6042. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab270. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33905522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interaction between coumarin drugs and DNA gyrase.Mol Microbiol. 1993 Aug;9(4):681-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01728.x. Mol Microbiol. 1993. PMID: 8231802 Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo and in vitro patterns of the activity of simocyclinone D8, an angucyclinone antibiotic from Streptomyces antibioticus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009 May;53(5):2110-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01440-08. Epub 2009 Mar 9. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009. PMID: 19273673 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Helicobacter pylori Activity of Isocoumarin Paepalantine: Morphological and Molecular Docking Analysis.Molecules. 2017 May 12;22(5):786. doi: 10.3390/molecules22050786. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28498343 Free PMC article.
-
Accumulation of mutations in both gyrB and parE genes is associated with high-level resistance to novobiocin in Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 Sep;49(9):3810-5. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.9.3810-3815.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 16127057 Free PMC article.
-
Novobiocin Susceptibility of MukBEF-Deficient Escherichia coli Is Combinatorial with Efflux and Resides in DNA Topoisomerases.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Apr 22;60(5):2949-53. doi: 10.1128/AAC.03102-15. Print 2016 May. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 26926630 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of the ATP binding site of ParE to susceptibility to novobiocin and quinolones in Streptococcus pneumoniae.J Bacteriol. 2005 Feb;187(4):1536-40. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.4.1536-1540.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 15687222 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown, P. O., and N. R. Cozzarelli. 1979. A sign inversion mechanism for enzymatic supercoiling of DNA. Science 206:1081-1083. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2002. Vancomycin resistant Staphylococcus aureus—Pennsylvania, 2002. JAMA 288:2116.. - PubMed
-
- Chen, C. R., M. Malik, M. Snyder, and K. Drlica. 1996. DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV on the bacterial chromosome: quinolone-induced DNA cleavage. J. Mol. Biol. 258:627-637. - PubMed
-
- Chopra, I., L. Hesse, and A. J. O'Neill. 2002. Exploiting current understanding of antibiotic action for discovery of new drugs. J. Appl. Microbiol. 92(Suppl.):4S-15S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

