Novel missense mutations and a 288-bp exonic insertion in PAX9 in families with autosomal dominant hypodontia
- PMID: 12605438
- PMCID: PMC6156786
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.a.10011
Novel missense mutations and a 288-bp exonic insertion in PAX9 in families with autosomal dominant hypodontia
Abstract
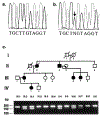
We describe the molecular analysis of three families with hypodontia involving primarily molar teeth and report two novel mutational mechanisms. Linkage analysis of two large families revealed that the hypodontia was linked to the PAX9 locus. These two families revealed missense mutations consisting of a glutamic acid substitution for lysine and a proline substitution for leucine within the paired domain of PAX9. A pair of identical twins affected with hypodontia in a third family demonstrated a 288-bp insertion within exon 2 that resulted in a putative frameshift mutation and a premature stop codon. The insertion was associated with the loss of 7-bp from exon 2. A block of 256-bp of sequence within the insertion was completely identical to downstream sequence from the second intron of the PAX9 gene. These studies extend the spectrum of mutations in PAX9 associated with hypodontia to include heretofore undescribed categories, including missense mutations.
Copyright 2003 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures




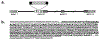

References
-
- Arte S, Nieminen P, Pirinen S, Thesleff I, Peltonen L. 1996. Gene defect in hypodontia: Exclusion of EGF, EGFR, and FGF-3 as candidate genes. J Dent Res 76:1346–1352. - PubMed
-
- Das P, Stockton DW, Bauer C, Shaffer LG, D’Souza RN, Wright JT, Patel PI. 2002. Haploinsufficiency of PAX9 is associated with autosomal dominant hypodontia. Hum Genet 110:371–376. - PubMed
-
- Frazier-Bowers SA, Guo DC, Cavender A, Xue L, Evans B, King T, Milewicz D, D’Souza RN. 2002. A novel mutation in human PAX9 causes molar oligodontia. J Dent Res 81:129–133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

